Oncogenic activation of NF-kappaB
- PMID: 20516126
- PMCID: PMC2869521
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000109
Oncogenic activation of NF-kappaB
Abstract
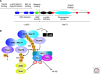
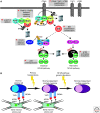
Recent genetic evidence has established a pathogenetic role for NF-kappaB signaling in cancer. NF-kappaB signaling is engaged transiently when normal B lymphocytes respond to antigens, but lymphomas derived from these cells accumulate genetic lesions that constitutively activate NF-kappaB signaling. Many genetic aberrations in lymphomas alter CARD11, MALT1, or BCL10, which constitute a signaling complex that is intermediate between the B-cell receptor and IkappaB kinase. The activated B-cell-like subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma activates NF-kappaB by a variety of mechanisms including oncogenic mutations in CARD11 and a chronic active form of B-cell receptor signaling. Normal plasma cells activate NF-kappaB in response to ligands in the bone marrow microenvironment, but their malignant counterpart, multiple myeloma, sustains a variety of genetic hits that stabilize the kinase NIK, leading to constitutive activation of the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways. Various oncogenic abnormalities in epithelial cancers, including mutant K-ras, engage unconventional IkappaB kinases to activate NF-kappaB. Inhibition of constitutive NF-kappaB signaling in each of these cancer types induces apoptosis, providing a rationale for the development of NF-kappaB pathway inhibitors for the treatment of cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Adams J 2004. The proteasome: a suitable antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer 4:349–360 - PubMed
-
- Akagi T, Motegi M, Tamura A, Suzuki R, Hosokawa Y, Suzuki H, Ota H, Nakamura S, Morishima Y, Taniwaki M, et al.1999. A novel gene, MALT1 at 18q21, is involved in t(11;18) (q21;q21) found in low-grade B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Oncogene 18:5785–5794 - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, et al.2000. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511 - PubMed
-
- Baens M, Fevery S, Sagaert X, Noels H, Hagens S, Broeckx V, Billiau AD, De Wolf-Peeters C, Marynen P 2006. Selective expansion of marginal zone B cells in Emicro-API2-MALT1 mice is linked to enhanced IkappaB kinase gamma polyubiquitination. Cancer Res 66:5270–5277 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
