The origins and evolution of the p53 family of genes
- PMID: 20516129
- PMCID: PMC2869528
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001198
The origins and evolution of the p53 family of genes
Abstract
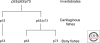
A common ancestor to the three p53 family members of human genes p53, p63, and p73 is first detected in the evolution of modern-day sea anemones, in which both structurally and functionally it acts to protect the germ line from genomic instabilities in response to stresses. This p63/p73 common ancestor gene is found in almost all invertebrates and first duplicates to produce a p53 gene and a p63/p73 ancestor in cartilaginous fish. Bony fish contain all three genes, p53, p63, and p73, and the functions of these three transcription factors diversify in the higher vertebrates. Thus, this gene family has preserved its structural features and functional activities for over one billion years of evolution.
Figures

References
-
- Agami R, Blandino G, Oren M, Shaul Y 1999. Interaction of c-Abl and p73α and their collaboration to induce apoptosis. Nature 399:809–813 - PubMed
-
- Arum O, Johnson TE 2007. Reduced expression of the Caenorhabditis elegans p53 ortholog cep-1 results in increased longevity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 62:951–959 - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Rowan S, Vousden KH 1996. Characterisation of human cyclin G1 and G2: DNA damage inducible genes. Oncogene 13:1103–1109 - PubMed
-
- Bensaad K, Tsuruta A, Selak MA, Vidal MN, Nakano K, Bartrons R, Gottlieb E, Vousden KH 2006. TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 126:107–120 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
