MicroRNA-140 and the silencing of osteoarthritis
- PMID: 20516192
- PMCID: PMC2878645
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1939310
MicroRNA-140 and the silencing of osteoarthritis
Abstract
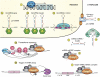
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important modulators in development, tissue homeostasis, and diseases. In this issue of Genes & Development, Miyaki and colleagues (pp. 1173-1185) report that miR-140 is involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by regulating, at least in part, ADAMTS5. Moreover, mice lacking miR-140 are dwarf as a consequence of impaired chondrocyte proliferation. This study is the first in vivo demonstration that miR-140 has a critical and nonredundant role in cartilage development and homeostasis.
Figures

Comment on
-
MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and homeostasis.Genes Dev. 2010 Jun 1;24(11):1173-85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1915510. Epub 2010 May 13. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20466812 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and homeostasis.Genes Dev. 2010 Jun 1;24(11):1173-85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1915510. Epub 2010 May 13. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20466812 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MALAT1/MiR-145 Adjusts IL-1β-Induced Chondrocytes Viability and Cartilage Matrix Degradation by Regulating ADAMTS5 in Human Osteoarthritis.Yonsei Med J. 2019 Nov;60(11):1081-1092. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.11.1081. Yonsei Med J. 2019. PMID: 31637891 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate modulates global microRNA expression in interleukin-1β-stimulated human osteoarthritis chondrocytes: potential role of EGCG on negative co-regulation of microRNA-140-3p and ADAMTS5.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Apr;57(3):917-928. doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1375-x. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28110479
-
Molecular mechanisms of the cartilage-specific microRNA-140 in osteoarthritis.Inflamm Res. 2013 Oct;62(10):871-7. doi: 10.1007/s00011-013-0654-8. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Inflamm Res. 2013. PMID: 23942573 Review.
-
Modulated Autophagy by MicroRNAs in Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes.Biomed Res Int. 2019 May 8;2019:1484152. doi: 10.1155/2019/1484152. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31205933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced miR‑26a and miR‑26b expression contributes to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis via the promotion of p65 translocation.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Feb;15(2):551-558. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.6035. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28000846 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of both miR-140-3p and miR-140-5p in synovial fluid correlate with osteoarthritis severity.Bone Joint Res. 2017 Nov;6(11):612-618. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.611.BJR-2017-0090.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2017. PMID: 29092816 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in cartilage development and dysplasia.Bone. 2020 Nov;140:115564. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115564. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Bone. 2020. PMID: 32745689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effects of cartilage progenitor cells and microRNA-140 on repair of osteoarthritic cartilage injury].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 May 15;33(5):650-658. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201806060. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31090363 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Urchin-like ceria nanoparticles for enhanced gene therapy of osteoarthritis.Sci Adv. 2023 Jun 16;9(24):eadf0988. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf0988. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37315130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ameye LG, Young MF 2006. Animal models of osteoarthritis: Lessons learned while seeking the ‘Holy Grail.’ Curr Opin Rheumatol 18: 537–547 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP 2004. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, Murchison EP, Alcorn H, Li MZ, Mills AA, Elledge SJ, Anderson KV, Hannon GJ 2003. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet 35: 215–217 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
