Break-induced replication requires all essential DNA replication factors except those specific for pre-RC assembly
- PMID: 20516198
- PMCID: PMC2878651
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1922610
Break-induced replication requires all essential DNA replication factors except those specific for pre-RC assembly
Abstract
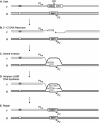
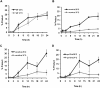
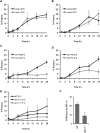
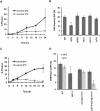
Break-induced replication (BIR) is an efficient homologous recombination (HR) pathway employed to repair a DNA double-strand break (DSB) when homology is restricted to one end. All three major replicative DNA polymerases are required for BIR, including the otherwise nonessential Pol32 subunit. Here we show that BIR requires the replicative DNA helicase (Cdc45, the GINS, and Mcm2-7 proteins) as well as Cdt1. In contrast, both subunits of origin recognition complex (ORC) and Cdc6, which are required to create a prereplication complex (pre-RC), are dispensable. The Cdc7 kinase, required for both initiation of DNA replication and post-replication repair (PRR), is also required for BIR. Ubiquitination and sumoylation of the DNA processivity clamp PCNA play modest roles; in contrast, PCNA alleles that suppress pol32Delta's cold sensitivity fail to suppress its role in BIR, and are by themselves dominant inhibitors of BIR. These results suggest that origin-independent BIR involves cross-talk between normal DNA replication factors and PRR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiple Cdt1 molecules act at each origin to load replication-competent Mcm2-7 helicases.EMBO J. 2011 Nov 1;30(24):4885-96. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.394. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 22045335 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the contributions of helicases to break-induced replication.Methods Enzymol. 2022;672:339-368. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2022.02.025. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Methods Enzymol. 2022. PMID: 35934483
-
Break-induced replication and telomerase-independent telomere maintenance require Pol32.Nature. 2007 Aug 16;448(7155):820-3. doi: 10.1038/nature06047. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17671506
-
Break-induced replication: unraveling each step.Trends Genet. 2022 Jul;38(7):752-765. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2022.03.011. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Trends Genet. 2022. PMID: 35459559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of chromosomal DNA replication initiation and replication fork stabilization in eukaryotes.Sci China Life Sci. 2014 May;57(5):482-7. doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4631-4. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Sci China Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24699916 Review.
Cited by
-
Limiting homologous recombination at stalled replication forks is essential for cell viability: DNA2 to the rescue.Curr Genet. 2020 Dec;66(6):1085-1092. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01106-7. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32909097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Many Roles of PCNA in Eukaryotic DNA Replication.Enzymes. 2016;39:231-54. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Enzymes. 2016. PMID: 27241932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Break-induced replication: functions and molecular mechanism.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Jun;23(3):271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23790415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian chromosomes contain cis-acting elements that control replication timing, mitotic condensation, and stability of entire chromosomes.Bioessays. 2012 Sep;34(9):760-70. doi: 10.1002/bies.201200035. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Bioessays. 2012. PMID: 22706734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conservation and Variation in Strategies for DNA Replication of Kinetoplastid Nuclear Genomes.Curr Genomics. 2018 Feb;19(2):98-109. doi: 10.2174/1389202918666170815144627. Curr Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29491738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arias EE, Walter JC 2007. Strength in numbers: Preventing rereplication via multiple mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. Genes Dev 21: 497–518 - PubMed
-
- Ballabeni A, Zamponi R, Caprara G, Melixetian M, Bossi S, Masiero L, Helin K 2009. Human CDT1 associates with CDC7 and recruits CDC45 to chromatin during S phase. J Biol Chem 284: 3028–3036 - PubMed
-
- Bergink S, Jentsch S 2009. Principles of ubiquitin and SUMO modifications in DNA repair. Nature 458: 461–467 - PubMed
-
- Branzei D, Vanoli F, Foiani M 2008. SUMOylation regulates Rad18-mediated template switch. Nature 456: 915–920 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
