Bag1-L is a phosphorylation-dependent coactivator of c-Jun during neuronal apoptosis
- PMID: 20516211
- PMCID: PMC2916400
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01610-09
Bag1-L is a phosphorylation-dependent coactivator of c-Jun during neuronal apoptosis
Abstract
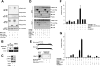
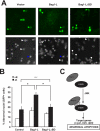
In the nervous system, cell death by apoptosis plays a critical role during normal development and pathological neurodegeneration. Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) are essential regulators of neuronal apoptosis. The AP-1 transcription factor c-Jun is phosphorylated at multiple sites within its transactivation domain by the JNKs, and c-Jun phosphorylation is required for JNK-induced neurotoxicity. While the importance of c-Jun as a mediator of apoptotic JNK signaling in neurons is firmly established, the molecular mechanism underlying the requirement for c-Jun N-terminal phosphorylation is enigmatic. Here we identify the multifunctional protein Bag1-L as a coactivator of phosphorylated c-Jun. Bag1-L preferentially interacts with N-terminally phosphorylated c-Jun, and Bag1-L greatly augments transcriptional activation by phosphorylated c-Jun. Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments revealed binding of Bag1-L to the promoters of proapoptotic AP-1 target genes, and overexpression of Bag1-L augmented cell death in primary neurons. Therefore, Bag1-L functions as a coactivator regulating neurotoxicity mediated by phosphorylated c-Jun.
Figures




References
-
- Alberts, A. S., O. Geneste, and R. Treisman. 1998. Activation of SRF-regulated chromosomal templates by Rho-family GTPases requires a signal that also induces H4 hyperacetylation. Cell 92:475-487. - PubMed
-
- Angel, P., K. Hattori, T. Smeal, and M. Karin. 1988. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP1. Cell 55:875-885. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, J. D., N. J. Arhel, S. S. Lee, A. Sharp, M. Al-Okail, G. Packham, A. Hague, C. Paraskeva, and A. C. Williams. 2005. Nuclear BAG-1 expression inhibits apoptosis in colorectal adenoma-derived epithelial cells. Apoptosis 10:301-311. - PubMed
-
- Behrens, A., M. Sibilia, and E. F. Wagner. 1999. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat. Genet. 21:326-329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
