mTORC1 directly phosphorylates and regulates human MAF1
- PMID: 20516213
- PMCID: PMC2916396
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00319-10
mTORC1 directly phosphorylates and regulates human MAF1
Abstract
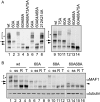
mTORC1 is a central regulator of growth in response to nutrient availability, but few direct targets have been identified. RNA polymerase (pol) III produces a number of essential RNA molecules involved in protein synthesis, RNA maturation, and other processes. Its activity is highly regulated, and deregulation can lead to cell transformation. The human phosphoprotein MAF1 becomes dephosphorylated and represses pol III transcription after various stresses, but neither the significance of the phosphorylations nor the kinase involved is known. We find that human MAF1 is absolutely required for pol III repression in response to serum starvation or TORC1 inhibition by rapamycin or Torin1. The protein is phosphorylated mainly on residues S60, S68, and S75, and this inhibits its pol III repression function. The responsible kinase is mTORC1, which phosphorylates MAF1 directly. Our results describe molecular mechanisms by which mTORC1 controls human MAF1, a key repressor of RNA polymerase III transcription, and add a new branch to the signal transduction cascade immediately downstream of TORC1.
Figures

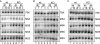

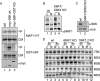

Similar articles
-
General repression of RNA polymerase III transcription is triggered by protein phosphatase type 2A-mediated dephosphorylation of Maf1.Mol Cell. 2006 Jun 9;22(5):623-32. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.04.008. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16762835
-
Recovery of RNA polymerase III transcription from the glycerol-repressed state: revisiting the role of protein kinase CK2 in Maf1 phosphoregulation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 31;287(36):30833-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.378828. Epub 2012 Jul 18. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22810236 Free PMC article.
-
Maf1, a new player in the regulation of human RNA polymerase III transcription.PLoS One. 2006 Dec 27;1(1):e134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000134. PLoS One. 2006. PMID: 17205138 Free PMC article.
-
Maf1 regulation: a model of signal transduction inside the nucleus.Nucleus. 2010 Mar-Apr;1(2):162-5. doi: 10.4161/nucl.1.2.11179. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Nucleus. 2010. PMID: 21326948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAF1: a new target of mTORC1.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Apr;39(2):487-91. doi: 10.1042/BST0390487. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21428925 Review.
Cited by
-
Body size regulation and insulin-like growth factor signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jul;70(13):2351-65. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1313-5. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23508807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maf1 regulates intracellular lipid homeostasis in response to DNA damage response activation.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 May 15;32(11):1086-1093. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-06-0378. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33788576 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila RNA polymerase III repressor Maf1 controls body size and developmental timing by modulating tRNAiMet synthesis and systemic insulin signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 24;109(4):1139-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113311109. Epub 2012 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22228302 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of Maf1 protein controls RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription repression.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 28;288(26):19288-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.473744. Epub 2013 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23673667 Free PMC article.
-
The mTORC1-eIF4F axis controls paused pluripotency.EMBO Rep. 2022 Feb 3;23(2):e53081. doi: 10.15252/embr.202153081. Epub 2021 Dec 6. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 34866316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dennis, P. B., A. Jaeschke, M. Saitoh, B. Fowler, S. C. Kozma, and G. Thomas. 2001. Mammalian TOR: a homeostatic ATP sensor. Science 294:1102-1105. - PubMed
-
- De Virgilio, C., and R. Loewith. 2006. Cell growth control: little eukaryotes make big contributions. Oncogene 25:6392-6415. - PubMed
-
- Djouder, N., S. C. Metzler, A. Schmidt, C. Wirbelauer, M. Gstaiger, R. Aebersold, D. Hess, and W. Krek. 2007. S6K1-mediated disassembly of mitochondrial URI/PP1gamma complexes activates a negative feedback program that counters S6K1 survival signaling. Mol. Cell 28:28-40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
