Partition profile of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in lipid domains upon reconstitution
- PMID: 20516251
- PMCID: PMC2918924
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M005132
Partition profile of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in lipid domains upon reconstitution
Abstract
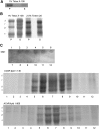
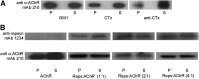
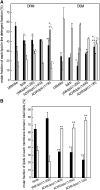
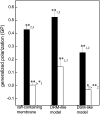
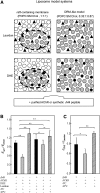
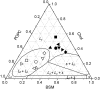
The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) is in intimate contact with the lipids in its native membrane. Here we analyze the possibility that it is the intrinsic properties of the AChR that determine its partition into a given lipid domain. Torpedo AChR or a synthetic peptide corresponding to the AChR M4 segment (the one in closer contact with lipids) was reconstituted into "raft"-containing model membranes. The distribution of the AChR was assessed by Triton X-100 extraction in combination with fluorescence studies, and lipid analyses were performed on each sample. The influence of rapsyn, a peripheral protein involved in AChR aggregation, was studied. Raft-like domain aggregation was also studied using membranes containing the ganglioside GM1 followed by GM1 crosslinking. The gammaM4 peptide displays a marked preference for raft-like domains. In contrast, AChR alone or in the presence of rapsyn or ganglioside aggregation exhibits no such preference for raft-like domains, but it does cause a significant reduction in the total amount of these domains. The results indicate that the distribution of the AChR in lipid domains cannot be due exclusively to the intrinsic physicochemical properties of the protein and that there must be an external signal in native cell membranes that directs the AChR to a specific membrane domain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The steroid promegestone is a noncompetitive antagonist of the Torpedo nicotinic acetylcholine receptor that interacts with the lipid-protein interface.Mol Pharmacol. 1999 Feb;55(2):269-78. doi: 10.1124/mol.55.2.269. Mol Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 9927618
-
Physical state of bulk and protein-associated lipid in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-rich membrane studied by laurdan generalized polarization and fluorescence energy transfer.Biophys J. 1996 Mar;70(3):1275-84. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79684-4. Biophys J. 1996. PMID: 8785283 Free PMC article.
-
Transbilayer asymmetry and sphingomyelin composition modulate the preferential membrane partitioning of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in Lo domains.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Feb 1;591:76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.12.003. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016. PMID: 26702544
-
Lipid matters: nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-lipid interactions (Review).Mol Membr Biol. 2002 Oct-Dec;19(4):277-84. doi: 10.1080/09687680210166226. Mol Membr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12512774 Review.
-
Protein-promoted membrane domains.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jul-Aug;1778(7-8):1583-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.01.021. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18294450 Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral pressure-mediated protein partitioning into liquid-ordered/liquid-disordered domains.Soft Matter. 2016 Apr 7;12(13):3189-95. doi: 10.1039/c6sm00042h. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Soft Matter. 2016. PMID: 27003910 Free PMC article.
-
Boundary lipids of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: Spontaneous partitioning via coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulation.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019 Apr 1;1861(4):887-896. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.01.005. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 30664881 Free PMC article.
-
Carlos Gutiérrez-Merino: Synergy of Theory and Experimentation in Biological Membrane Research.Molecules. 2024 Feb 10;29(4):820. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040820. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid rafts and Alzheimer's disease: protein-lipid interactions and perturbation of signaling.Front Physiol. 2012 Jun 22;3:189. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00189. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22737128 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of a rapid neurotransmitter receptor-ion channel by membrane lipids.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 11;11:1328875. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1328875. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38274273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrantes F. J. 2004. Structural basis for lipid modulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 47: 71–95. - PubMed
-
- Barrantes F. J. 2003. Modulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function through the outer and middle rings of transmembrane domains. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 6: 620–632. - PubMed
-
- Sanes J. R., Lichtman J. W. 2001. Induction, assembly, maturation and maintenance of a postsynaptic apparatus. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2: 791–805. - PubMed
-
- Moransard M., Borges L. S., Willmann R., Marangi P. A., Brenner H. R., Ferns M. J., Fuhrer C. 2003. Agrin regulates rapsyn interaction with surface acetylcholine receptors, and this underlies cytoskeletal anchoring and clustering. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 7350–7359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

