Endothelial-derived tissue factor pathway inhibitor regulates arterial thrombosis but is not required for development or hemostasis
- PMID: 20516367
- PMCID: PMC2947398
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-10-250910
Endothelial-derived tissue factor pathway inhibitor regulates arterial thrombosis but is not required for development or hemostasis
Abstract
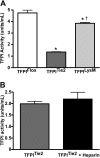
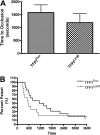
The antithrombotic surface of endothelium is regulated in a coordinated manner. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) localized at the endothelial cell surface regulates the production of FXa by inhibiting the TF/VIIa complex. Systemic homozygotic deletion of the first Kunitz (K1) domain of TFPI results in intrauterine lethality in mice. Here we define the cellular sources of TFPI and their role in development, hemostasis, and thrombosis using TFPI conditional knockout mice. We used a Cre-lox strategy and generated mice with a floxed exon 4 (TFPI(Flox)) which encodes for the TFPI-K1 domain. Mice bred into Tie2-Cre and LysM-Cre lines to delete TFPI-K1 in endothelial (TFPI(Tie2)) and myelomonocytic (TFPI(LysM)) cells resulted in viable and fertile offspring. Plasma TFPI activity was reduced in the TFPI(Tie2) (71% ± 0.9%, P < .001) and TFPI(LysM) (19% ± 0.6%, P < .001) compared with TFPI(Flox) littermate controls. Tail and cuticle bleeding were unaffected. However, TFPI(Tie2) mice but not TFPI(LysM) mice had increased ferric chloride-induced arterial thrombosis. Taken together, the data reveal distinct roles for endothelial- and myelomonocytic-derived TFPI.
Figures



Comment in
-
Balancing clotting.Blood. 2010 Sep 9;116(10):1634-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-289918. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20829379 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosenberg RD, Aird WC. Vascular-bed–specific hemostasis and hypercoagulable states. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(20):1555–1564. - PubMed
-
- Novotny WF, Girard TJ, Miletich JP, Broze GJ., Jr Purification and characterization of the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(31):18832–18837. - PubMed
-
- Novotny WF, Palmier M, Wun TC, Broze GJ, Jr, Miletich JP. Purification and properties of heparin-releasable lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Blood. 1991;78(2):394–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

