Effects of CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) inhibitors on the dynamics of CCR5 and CC-chemokine-CCR5 interactions
- PMID: 20516552
- PMCID: PMC6540997
- DOI: 10.3851/IMP1529
Effects of CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) inhibitors on the dynamics of CCR5 and CC-chemokine-CCR5 interactions
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to examine how CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) inhibitors (aplaviroc [APL], TAK779 and maraviroc [MVC]) interact with CCR5 and affect its dynamics and physiological CC-chemokine-CCR5 interactions.
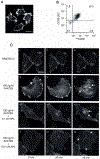
Methods: A yellow fluorescent protein (YFP)-tagged CCR5-expressing U373-MAGI cell line was generated and a stable CCR5-expressing clonal population, (YFP)CCR5-UM16, was prepared. (YFP)CCR5-UM16 cells were exposed to RANTES, macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha or MIP-1beta (all 100 ng/ml) with or without CCR5 inhibitors and (YFP)CCR5 internalization was visualized with real-time by laser scanning confocal microscopy. The mobility of (YFP)CCR5 was also examined in the presence of CCR5 inhibitors with fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) imaging.
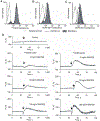
Results: Following the addition of each CC chemokine, intracellular fluorescence intensity increased whereas membranous fluorescence decreased, signifying (YFP)CCR5 internalization. All three CCR5 inhibitors failed to induce (YFP)CCR5 internalization. All three CCR5 inhibitors blocked the CC-chemokine-induced internalization at a high concentration of 1 microM; however, the ratio of APL concentration that blocked RANTES-induced internalization by 50% over APL concentration that blocked HIV type-1 (HIV-1) replication by 50% was 16.4, indicating that APL permits CC-chemokine-induced internalization to a much greater extent compared with TAK779 and MVC, having ratios of 1.1 and 0.9, respectively. The examination of (YFP)CCR5 mobility with FRAP imaging revealed that (YFP)CCR5 continuously underwent rapid redistribution, which none of the three inhibitors blocked.
Conclusions: The finding that APL moderately blocked the RANTES-triggered (YFP)CCR5 internalization despite the highly potent anti-HIV-1 activity of APL strongly suggests that development of CCR5 inhibitors, which do not overly inhibit physiological CC-chemokine-CCR5 interactions, is practically feasible.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular interactions of CCR5 with major classes of small-molecule anti-HIV CCR5 antagonists.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;73(3):789-800. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.042101. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18096812
-
Spirodiketopiperazine-based CCR5 inhibitor which preserves CC-chemokine/CCR5 interactions and exerts potent activity against R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro.J Virol. 2004 Aug;78(16):8654-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8654-8662.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15280474 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist-induced internalization of CC chemokine receptor 5 as a mechanism to inhibit HIV replication.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Jun;337(3):655-62. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.179622. Epub 2011 Mar 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21389095
-
[Viral entry as therapeutic target. Current situation of entry inhibitors].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008 Oct;26 Suppl 11:5-11. doi: 10.1016/s0213-005x(08)76557-1. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008. PMID: 19133215 Review. Spanish.
-
[Pharmacokinetics, interactions and mechanism of action of maraviroc].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008 Oct;26 Suppl 11:12-6. doi: 10.1016/s0213-005x(08)76558-3. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008. PMID: 19133216 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Immunological and pharmacological strategies to reactivate HIV-1 from latently infected cells: a possibility for HIV-1 paediatric patients?J Virus Erad. 2015 Jul 1;1(3):148-52. doi: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30508-2. J Virus Erad. 2015. PMID: 27482406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity and structural analysis of GRL-117C: a novel small molecule CCR5 inhibitor active against R5-tropic HIV-1s.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 18;9(1):4828. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41080-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30886166 Free PMC article.
-
The immunologic effects of maraviroc intensification in treated HIV-infected individuals with incomplete CD4+ T-cell recovery: a randomized trial.Blood. 2013 Jun 6;121(23):4635-46. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-436345. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23589670 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder CC, et al. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macropliage-tropic HIV-1. Science 1996; 272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Raport CJ, Gosling J, Schweickart VL, Gray PW, Charo IF. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel human CC chemokine receptor (CCR5) for RANTES, MIP-1beta, and MIP-1alpha. J Biol Chem 1996; 271:17161–17166. - PubMed
-
- Wu L, Gerard NP, Wyatt R, et al. CD4-induced interaction of primary HIV-1 gp120 glycoproteins with the chemokine receptor CCR-5. Nature 1996; 384:179–183. - PubMed
-
- Kilby JM, Eron JJ. Novel therapies based on mechanisms of HIV-1 cell entry. N Engl J Med 2003; 348:2228–2238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

