MicroRNAs as biomarkers in rheumatic diseases
- PMID: 20517293
- PMCID: PMC3041596
- DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.81
MicroRNAs as biomarkers in rheumatic diseases
Abstract
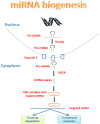
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous, noncoding, single-stranded RNAs of 19-25 nucleotides in length. They regulate gene expression and are important in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes. MiRNAs are attractive as potential biomarkers because their expression pattern is reflective of underlying pathophysiologic processes and they are specific to various disease states. Moreover, miRNAs can be detected in a variety of sources, including tissue, blood and body fluids; they are reasonably stable and appear to be resistant to differences in sample handling, which increases their appeal as practical biomarkers. The clinical utility of miRNAs as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers has been demonstrated in various malignancies and a few nonmalignant diseases. There is accumulating evidence that miRNAs have an important role in systemic rheumatic diseases and that various diseases or different stages of the same disease are associated with distinct miRNA expression profiles. Preliminary data suggest that miRNAs are promising as candidate biomarkers of diagnosis, prognosis, disease activity and severity in autoimmune diseases. MiRNAs identified as potential biomarkers in pilot studies should be validated in larger studies designed specifically for biomarker validation.
Figures

References
-
- Chua JH, Armugam A, Jeyaseelan K. MicroRNAs: biogenesis, function and applications. Current Opinion in Molecular Therapeutics. 2009;11:189–99. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54. - PubMed
-
- Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–8. - PubMed
-
- Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–62. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans.[see comment] Science. 2001;294:862–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

