Insulin-like growth factors and risk of kidney cancer in men
- PMID: 20517306
- PMCID: PMC2905287
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605722
Insulin-like growth factors and risk of kidney cancer in men
Abstract
Background: Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) has been shown to increase kidney growth, glomerular filtration rate, and renal function.
Methods: In the prospective Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention (ATBC) study of 29 133 Finnish male smokers aged 50-69 years, serum concentrations of IGF were measured in samples collected in 1985-1988. A total of 100 men with kidney cancer diagnosed > or =5 years after blood collection through 1997 were compared with a subcohort of 400 men; logistic regression models were used to estimate the risk of developing kidney cancer.
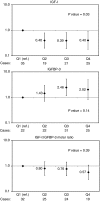
Results: Men with IGF-I levels >113 ng ml(-1) were 59% less likely to develop kidney cancer than men with levels < or =113 ng ml(-1) (odds ratio=0.41; 95% confidence interval=0.23-0.75). The IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) levels did not alter the association. No association was observed between IGFBP-3, or molar ratio of IGF-I/IGFBP-3, and kidney cancer.
Conclusions: Low serum IGF-I levels in this cohort of older middle-aged male smokers are associated with increased kidney cancer risk, independent of IGFBP-3.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor I, binding proteins -1 and -3, risk of type 2 diabetes and macronutrient intakes in men.Br J Nutr. 2019 Apr;121(8):938-944. doi: 10.1017/S0007114519000321. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Br J Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30898176 Clinical Trial.
-
Insulin-like growth factor I, IGF-binding protein 3, and lung cancer risk in a prospective study of men in China.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002 May 15;94(10):749-54. doi: 10.1093/jnci/94.10.749. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002. PMID: 12011225
-
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-binding protein-3, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004 Mar;13(3):438-44. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004. PMID: 15006921
-
Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000 Dec 6;92(23):1910-7. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.23.1910. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000. PMID: 11106682
-
Serum insulin-like growth factor I: tumor marker or etiologic factor? A prospective study of prostate cancer among Finnish men.Cancer Res. 2003 Jul 15;63(14):3991-4. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12873996
Cited by
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling in renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 12;16:453. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2437-4. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27405474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factors and liver cancer risk in male smokers.Br J Cancer. 2010 Sep 28;103(7):1089-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605842. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20717109 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating levels of obesity-related markers and risk of renal cell carcinoma in the PLCO cancer screening trial.Cancer Causes Control. 2017 Jul;28(7):801-807. doi: 10.1007/s10552-017-0901-3. Epub 2017 May 8. Cancer Causes Control. 2017. PMID: 28484923 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes mellitus and incidence of kidney cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.Diabetologia. 2011 May;54(5):1013-8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2051-6. Epub 2011 Jan 28. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21274512
-
Glycemic index, glycemic load and carbohydrate intake in association with risk of renal cell carcinoma.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Oct 26;38(11):1129-1135. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx083. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28968893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society (2009) Cancer Facts and Figures. American Cancer Society: Atlanta
-
- Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P, Hennekens CH, Pollak M (1998) Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science 279(5350): 563–566 - PubMed
-
- Cheung CW, Vesey DA, Nicol DL, Johnson DW (2004) The roles of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in the regulation of proximal tubule, and renal cell carcinoma cell proliferation. Kidney Int 65(4): 1272–1279 - PubMed
-
- Chow WH, Gridley G, Fraumeni Jr JF, Jarvholm B (2000) Obesity, hypertension, and the risk of kidney cancer in men. N Engl J Med 343(18): 1305–1311 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous