Epidemiology of west nile in europe and in the mediterranean basin
- PMID: 20517490
- PMCID: PMC2878979
- DOI: 10.2174/1874357901004020029
Epidemiology of west nile in europe and in the mediterranean basin
Abstract
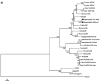
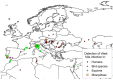
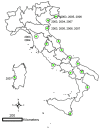
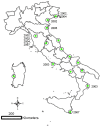
In the last 30 years several cases of West Nile (WN) virus infection were reported in horses and humans in Europe and in the Mediterranean Basin. Most of them were determined by strains of the Lineage 1 included in the European Mediterranean/Kenyan cluster. Strains of this cluster are characterised by a moderate pathogenicity for horses and humans and limited or no pathogenicity for birds. In recent years, however, WN cases determined by strains grouped in the Israeli/American cluster of Lineage 1 or in the lineage 2 have been reported in Hungary and Austria. The role of migrating birds in introducing new viruses to Europe has been often demonstrated. The migratory birds, which may be infected in their African wintering places, carry the virus northward to European sites during spring migrations. In the past, the virus introduction determined occasional cases of WN. In the recent years, new epidemiological scenarios are developing. In few occasions it has been evidenced the capability of WNV strains of overwintering by using local birds and mosquitoes. Species of Culex amongst mosquitoes and magpies (Pica pica), carrion crows (Corvus corone) and rock pigeons (Columba livia) amongst resident birds are the most probable species involved in this hypothetical WND endemic cycle.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Europe; Mediterranean Basin; West Nile..
Figures
References
-
- Karabatsos N. International catalogue of arboviruses, including certain other viruses of vertebrates. 3rd. San Antonio: American Society of Tropical Medicine & Hygiene; 1985. - PubMed
-
- Komar N. West Nile viral encephalitis. Rev Sci Tech. 2000;19:166–76. - PubMed
-
- Lanciotti RS, Roehrig JT, Deubel V, et al. Origin of the West Nile virus responsible for an outbreak of encephalitis in the northeastern United States. Science. 1999;286:2333–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
