Meeting report: applied biopharmaceutics and quality by design for dissolution/release specification setting: product quality for patient benefit
- PMID: 20517660
- PMCID: PMC2895441
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-010-9206-0
Meeting report: applied biopharmaceutics and quality by design for dissolution/release specification setting: product quality for patient benefit
Abstract
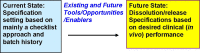
A biopharmaceutics and Quality by Design (QbD) conference was held on June 10-12, 2009 in Rockville, Maryland, USA to provide a forum and identify approaches for enhancing product quality for patient benefit. Presentations concerned the current biopharmaceutical toolbox (i.e., in vitro, in silico, pre-clinical, in vivo, and statistical approaches), as well as case studies, and reflections on new paradigms. Plenary and breakout session discussions evaluated the current state and envisioned a future state that more effectively integrates QbD and biopharmaceutics. Breakout groups discussed the following four topics: Integrating Biopharmaceutical Assessment into the QbD Paradigm, Predictive Statistical Tools, Predictive Mechanistic Tools, and Predictive Analytical Tools. Nine priority areas, further described in this report, were identified for advancing integration of biopharmaceutics and support a more fundamentally based, integrated approach to setting product dissolution/release acceptance criteria. Collaboration among a broad range of disciplines and fostering a knowledge sharing environment that places the patient's needs as the focus of drug development, consistent with science- and risk-based spirit of QbD, were identified as key components of the path forward.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Biopharmaceutics Classification System: subclasses for in vivo predictive dissolution (IPD) methodology and IVIVC.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014 Jun 16;57:152-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 24486482 Free PMC article.
-
Best Practices in the Development and Validation of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling. A Workshop Summary Report.J Pharm Sci. 2021 Feb;110(2):584-593. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2020.09.058. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33058891
-
Dissolution and Translational Modeling Strategies Toward Establishing an In Vitro-In Vivo Link-a Workshop Summary Report.AAPS J. 2019 Feb 11;21(2):29. doi: 10.1208/s12248-019-0298-x. AAPS J. 2019. PMID: 30746576
-
Progressive tools and critical strategies for development of best fit PBPK model aiming better in vitro-in vivo correlation.Int J Pharm. 2023 Aug 25;643:123267. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123267. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37488057 Review.
-
Oral biopharmaceutics tools - time for a new initiative - an introduction to the IMI project OrBiTo.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014 Jun 16;57:292-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.10.012. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 24189462 Review.
Cited by
-
Statistical comparison of dissolution profiles to predict the bioequivalence of extended release formulations.AAPS J. 2014 Jul;16(4):791-801. doi: 10.1208/s12248-014-9615-6. Epub 2014 May 23. AAPS J. 2014. PMID: 24854895 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific and Regulatory Considerations in Solid Oral Modified Release Drug Product Development.AAPS J. 2016 Nov;18(6):1406-1417. doi: 10.1208/s12248-016-9974-2. Epub 2016 Sep 20. AAPS J. 2016. PMID: 27650190 Review.
-
Application of Absorption Modeling in Rational Design of Drug Product Under Quality-by-Design Paradigm.AAPS J. 2015 Sep;17(5):1224-36. doi: 10.1208/s12248-015-9781-1. Epub 2015 May 22. AAPS J. 2015. PMID: 26002509 Free PMC article.
-
Quality cell therapy manufacturing by design.Nat Biotechnol. 2016 Apr;34(4):393-400. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3525. Nat Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27054995
-
Summary workshop report: Facilitating oral product development and reducing regulatory burden through novel approaches to assess bioavailability/bioequivalence.AAPS J. 2012 Sep;14(3):627-38. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9376-z. Epub 2012 Jun 9. AAPS J. 2012. PMID: 22684402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guidance for Industry Q8(R2) Pharmaceutical development, 2009 (ICH Q8 (R2)). http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformati....
-
- Gray VA. Meeting report: University of Wisconsin/AAPS/FDA Workshop Applied Biopharmaceutics and Quality by Design for Dissolution/Release Specification Setting: Product Quality for Patient Benefit. Dissolution Technologies. 2009;16(4):35–39. - PubMed
-
- Müllertz A. Biorelevant dissolution media, biotechnology. Pharmaceutical aspects. Arlington: AAPS; 2007. pp. 151–177.
-
- Benet LZ, Wu CY. Using a biopharmaceutics drug disposition classification system to predict bioavailability and elimination characteristics of new molecular entities. Somerset: NJDMDG; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

