Soft drinks consumption and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 20518077
- PMCID: PMC2880768
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i21.2579
Soft drinks consumption and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
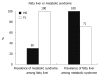
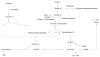
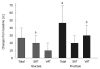
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common clinical condition which is associated with metabolic syndrome in 70% of cases. Inappropriate dietary fat intake, excessive intake of soft drinks, insulin resistance and increased oxidative stress combine to increase free fatty acid delivery to the liver, and increased hepatic triglyceride accumulation contributes to fatty liver. Regular soft drinks have high fructose corn syrup which contains basic sugar building blocks, fructose 55% and glucose 45%. Soft drinks are the leading source of added sugar worldwide, and have been linked to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. The consumption of soft drinks can increase the prevalence of NAFLD independently of metabolic syndrome. During regular soft drinks consumption, fat accumulates in the liver by the primary effect of fructose which increases lipogenesis, and in the case of diet soft drinks, by the additional contribution of aspartame sweetener and caramel colorant which are rich in advanced glycation end products that potentially increase insulin resistance and inflammation. This review emphasizes some hard facts about soft drinks, reviews fructose metabolism, and explains how fructose contributes to the development of obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and NAFLD.
Figures
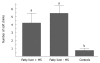
References
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, Marchesini G, Brunello F, Carucci P, Musso A, De Paolis P, Capussotti L, Salizzoni M, et al. Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Willner IR, Waters B, Patil SR, Reuben A, Morelli J, Riely CA. Ninety patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: insulin resistance, familial tendency, and severity of disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:2957–2961. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–1231. - PubMed
-
- Pi-Sunyer FX. The obesity epidemic: pathophysiology and consequences of obesity. Obes Res. 2002;10 Suppl 2:97S–104S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

