Cell cycle dependence of ionizing radiation-induced DNA deletions and antioxidant radioprotection in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 20518659
- PMCID: PMC3873222
- DOI: 10.1667/RR1661.1
Cell cycle dependence of ionizing radiation-induced DNA deletions and antioxidant radioprotection in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
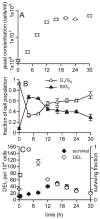
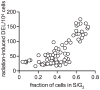
The yeast DEL assay is an effective method for measuring intrachromosomal recombination events resulting in DNA deletions that when occurring in mammalian cells are often associated with genomic instability and carcinogenesis. Here we used the DEL assay to measure gamma-ray-induced DNA deletions throughout different phases of yeast culture growth. Whereas yeast survival differed by only up to twofold throughout the yeast growth phase, proliferating cells in lag and early exponential growth phases were tenfold more sensitive to ionizing radiation-induced DNA deletions than cells in stationary phase. Radiation-induced DNA deletion potential was found to correlate directly with the fraction of cells in S/G(2) phase. The ability of the antioxidants l-ascorbic acid and DMSO to protect against radiation-induced DNA deletions was also measured within the different phases of yeast culture growth. Yeast cells in lag and early exponential growth phases were uniquely protected by antioxidant treatment, whereas nondividing cells in stationary phase could not be protected against the induction of DNA deletions. These results are compared with those from mammalian cell studies, and the implications for radiation-induced carcinogenesis and radioprotection are discussed.
Figures
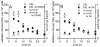
Similar articles
-
On the mechanism of UV and gamma-ray-induced intrachromosomal recombination in yeast cells synchronized in different stages of the cell cycle.Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Aug 21;248(3):301-10. doi: 10.1007/BF02191597. Mol Gen Genet. 1995. PMID: 7565592
-
Yeast DEL assay detects protection against radiation-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity: adaptation of a microtiter plate version.Radiat Res. 2010 Dec;174(6):719-26. doi: 10.1667/RR2059.1. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Radiat Res. 2010. PMID: 21128795 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of gamma-irradiation induced DNA damage and radioprotection of compounds in yeast using comet assay.J Radiat Res. 2004 Jun;45(2):169-74. doi: 10.1269/jrr.45.169. J Radiat Res. 2004. PMID: 15304956
-
Yeast strains to detect genomic deletions induced by carcinogens in cell-cycle arrested cells.Biotherapy. 1998;11(2-3):129-33. doi: 10.1023/a:1007978011313. Biotherapy. 1998. PMID: 9677044 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model organism for studying the carcinogenicity of non-ionizing electromagnetic fields and radiation].Mikrobiol Z. 2014 Jan-Feb;76(1):53-61. Mikrobiol Z. 2014. PMID: 24800516 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Effects of X-ray and carbon ion beam irradiation on membrane permeability and integrity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells.J Radiat Res. 2015 Mar;56(2):294-304. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru114. Epub 2015 Jan 18. J Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 25599994 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Photon Radiation on DNA Damage, Cell Proliferation, Cell Survival, and Apoptosis of Murine and Human Mesothelioma Cell Lines.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2022 Jul 21;7(6):101013. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2022.101013. eCollection 2022 Nov-Dec. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36420194 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity-Altered Adipose Stem Cells Promote Radiation Resistance of Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer through Paracrine Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2722. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082722. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326381 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the nanoscale motion rate of Candida albicans by X-rays.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 21;14:1133027. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1133027. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37025638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ward JF. DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:95–125. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Dent P, Grant S, Mikkelsen RB, Valerie K. Signal transduction and cellular radiation responses. Radiat Res. 2000;153:245–257. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Ojima M, Kodama S, Watanabe M. Radiation-induced DNA damage and delayed induced genomic instability. Oncogene. 2003;22:6988–6993. - PubMed
-
- Pouget JP, Mather SJ. General aspects of the cellular response to low- and high-LET radiation. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001;28:541–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

