With TOR, less is more: a key role for the conserved nutrient-sensing TOR pathway in aging
- PMID: 20519118
- PMCID: PMC2885591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.05.001
With TOR, less is more: a key role for the conserved nutrient-sensing TOR pathway in aging
Abstract
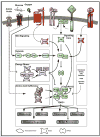
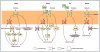
Target of rapamycin (TOR) is an evolutionarily conserved nutrient-sensing protein kinase that regulates growth and metabolism in all eukaryotic cells. Studies in flies, worms, yeast, and mice support the notion that the TOR signaling network modulates aging. TOR is also emerging as a robust mediator of the protective effects of various forms of dietary restriction (DR), which can extend life span and slow the onset of certain age-related diseases across species. Here we discuss how modulating TOR signaling slows aging through downstream processes including mRNA translation, autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signaling, stress responses, and metabolism. Identifying the mechanisms by which the TOR signaling network works as a pacemaker of aging is a major challenge and may help identify potential drug targets for age-related diseases, thereby facilitating healthful life span extension in humans.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilaniu H, Durieux J, Dillin A. Metabolism, ubiquinone synthesis, and longevity. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2399–2406. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar V, Alliouachene S, Sotiropoulos A, Sobering A, Athea Y, Djouadi F, Miraux S, Thiaudiere E, Foretz M, Viollet B, Diolez P, Bastin J, Benit P, Rustin P, Carling D, Sandri M, Ventura-Clapier R, Pende M. S6 kinase deletion suppresses muscle growth adaptations to nutrient availability by activating AMP kinase. Cell Metab. 2007;5:476–487. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Pearce LR, Garcia-Martinez JM. New insights into mTOR signaling: mTORC2 and beyond. Sci Signal. 2009;2:pe27. - PubMed
-
- Anisimov VN, Berstein LM, Egormin PA, Piskunova TS, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Tyndyk ML, Yurova MV, Kovalenko IG, Poroshina TE, Semenchenko AV. Metformin slows down aging and extends life span of female SHR mice. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2769–2773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

