Size mapping of electric field-assisted production of polycaprolactone particles
- PMID: 20519210
- PMCID: PMC2943887
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2010.0099.focus
Size mapping of electric field-assisted production of polycaprolactone particles
Abstract
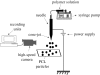
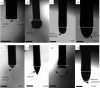
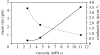
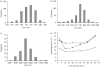
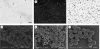
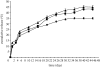
In this investigation, biodegradable polycaprolactone polymeric particles (300-4500 nm in diameter) were prepared by jetting a solution in an electric field. An extensive study has been carried out to determine how the size and size distribution of the particles generated can be controlled by systematically varying the polymer concentration in solution (and thereby its viscosity and electrical conductivity), and also the selected flow rate (2-50 microl min(-1)) and applied voltage (0-15 kV) during particle generation. Change in these parameters affects the mode of jetting, and within the stable cone-jet mode window, an increase in the applied voltage (approx. 15 kV) resulted in a reduction in particle size and this was more pronounced at high flow rates (such as; 30, 40 and 50 microl min(-1)) in the same region. The carrier particles were more polydisperse at the peripheral regions of the stable cone-jet mode, as defined in the applied voltage-flow rate parametric map. The effect of loading a drug on the particle size, size distribution and encapsulation efficiency was also studied. Release from drug-loaded particles was investigated using UV spectrophotometry over 45 days. This work demonstrates a powerful method of generating drug-loaded polymeric particles, with the ability to control size and polydispersivity, which has great potential in several categories of biotechnology requiring carrier particles, such as drug delivery and gene therapy.
Figures


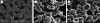
Similar articles
-
Preparation of budesonide-loaded polycaprolactone nanobeads by electrospraying for controlled drug release.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2011;22(18):2431-44. doi: 10.1163/092050610X540486. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2011. PMID: 21144167
-
Preparation of polymeric carriers for drug delivery with different shape and size using an electric jet.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009 Sep;10(6):600-8. doi: 10.2174/138920109789069323. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19619122
-
Electrospray encapsulation of water-soluble protein with polylactide. I. Effects of formulations and process on morphology and particle size.J Microencapsul. 2006 Feb;23(1):69-78. doi: 10.1080/02652040500435048. J Microencapsul. 2006. PMID: 16830978
-
Electrohydrodynamic atomisation driven design and engineering of opportunistic particulate systems for applications in drug delivery, therapeutics and pharmaceutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Sep;176:113788. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.04.026. Epub 2021 May 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33957180 Review.
-
A bird's eye view of nanoparticles prepared by electrospraying: advancements in drug delivery field.J Control Release. 2018 Sep 28;286:179-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.07.036. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30053427 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling Particle Formation: From Single Droplet Drying to Spray Drying and Electrospraying.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jul 4;12(7):625. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12070625. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32635464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation, Optimization and Activity Evaluation of PLGA/Streptokinase Nanoparticles Using Electrospray.Adv Pharm Bull. 2017 Apr;7(1):131-139. doi: 10.15171/apb.2017.017. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28507947 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling the heights--challenges in medical materials. Introduction.J R Soc Interface. 2010 Aug 6;7 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S377-8. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2010.0259.focus. Epub 2010 Jun 2. J R Soc Interface. 2010. PMID: 20519211 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Electrohydrodynamic atomization: A two-decade effort to produce and process micro-/nanoparticulate materials.Chem Eng Sci. 2015 Mar 24;125:32-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2014.08.061. Chem Eng Sci. 2015. PMID: 25684778 Free PMC article.
-
Progress of nanopreparation technology applied to volatile oil drug delivery systems.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 8;10(2):e24302. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24302. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. Retraction in: Heliyon. 2025 Feb 26;11(4):e42837. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42837. PMID: 38293491 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
References
-
- Borra J. P., Tombette Y., Ehouarn P. 1999. Influence of electric field profile and polarity on the mode of EHDA related to electric discharge regimes. J. Aerosol Sci. 30, 913–925. (10.1016/S0021-8502(98)00779-4) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

