Challenges of sequencing human genomes
- PMID: 20519329
- PMCID: PMC2980933
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbq016
Challenges of sequencing human genomes
Abstract
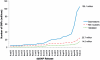
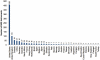
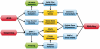
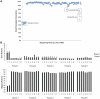
Massively parallel sequencing technologies continue to alter the study of human genetics. As the cost of sequencing declines, next-generation sequencing (NGS) instruments and datasets will become increasingly accessible to the wider research community. Investigators are understandably eager to harness the power of these new technologies. Sequencing human genomes on these platforms, however, presents numerous production and bioinformatics challenges. Production issues like sample contamination, library chimaeras and variable run quality have become increasingly problematic in the transition from technology development lab to production floor. Analysis of NGS data, too, remains challenging, particularly given the short-read lengths (35-250 bp) and sheer volume of data. The development of streamlined, highly automated pipelines for data analysis is critical for transition from technology adoption to accelerated research and publication. This review aims to describe the state of current NGS technologies, as well as the strategies that enable NGS users to characterize the full spectrum of DNA sequence variation in humans.
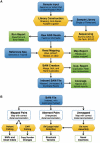
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

