Neurokinin B acts via the neurokinin-3 receptor in the retrochiasmatic area to stimulate luteinizing hormone secretion in sheep
- PMID: 20519368
- PMCID: PMC2940514
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-0174
Neurokinin B acts via the neurokinin-3 receptor in the retrochiasmatic area to stimulate luteinizing hormone secretion in sheep
Abstract
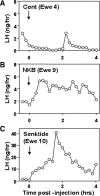
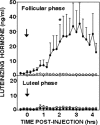
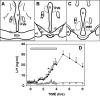
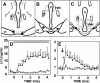
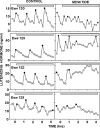
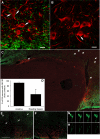
Recent data have demonstrated that mutations in the receptor for neurokinin B (NKB), the NK-3 receptor (NK3R), produce hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in humans. These data, together with reports that NKB expression increases after ovariectomy and in postmenopausal women, have led to the hypothesis that this tachykinin is an important stimulator of GnRH secretion. However, the NK3R agonist, senktide, inhibited LH secretion in rats and mice. In this study, we report that senktide stimulates LH secretion in ewes. A dramatic increase in LH concentrations to levels close to those observed during the preovulatory LH surge was observed after injection of 1 nmol senktide into the third ventricle during the follicular, but not in the luteal, phase. Similar increases in LH secretion occurred after insertion of microimplants containing this agonist into the retrochiasmatic area (RCh) in anestrous or follicular phase ewes. A low-dose microinjection (3 pmol) of senktide into the RCh produced a smaller but significant increase in LH concentrations in anestrous ewes. Moreover, NK3R immunoreactivity was clearly evident in the RCh, although it was not found in A15 dopaminergic cell bodies in this region. These data provide evidence that NKB stimulates LH (and presumably GnRH) secretion in ewes and point to the RCh as one important site of action. Based on these data, and the effects of NK3R mutations in humans, we hypothesize that NKB plays an important stimulatory role in the control of GnRH and LH secretion in nonrodent species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence that Neurokinin B Controls Basal Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Secretion but Is Not Critical for Estrogen-Positive Feedback in Sheep.Neuroendocrinology. 2015;101(2):161-74. doi: 10.1159/000377702. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Neuroendocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25677216
-
Neurokinin-3 receptor activation in the retrochiasmatic area is essential for the full pre-ovulatory luteinising hormone surge in ewes.J Neuroendocrinol. 2014 Nov;26(11):776-84. doi: 10.1111/jne.12180. J Neuroendocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25040132 Free PMC article.
-
Surge-Like Luteinising Hormone Secretion Induced by Retrochiasmatic Area NK3R Activation is Mediated Primarily by Arcuate Kisspeptin Neurones in the Ewe.J Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Jun;28(6):10.1111/jne.12393. doi: 10.1111/jne.12393. J Neuroendocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27059932 Free PMC article.
-
A role for neurokinin B in pulsatile GnRH secretion in the ewe.Neuroendocrinology. 2014;99(1):18-32. doi: 10.1159/000355285. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Neuroendocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24008670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of kisspeptin and neurokinin B in GnRH pulse generation in humans, and their potential clinical application.J Neuroendocrinol. 2022 May;34(5):e13081. doi: 10.1111/jne.13081. Epub 2021 Dec 28. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 34962670 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of prepubertal dynorphin secretion in the medial basal hypothalamus of the female rat.J Neuroendocrinol. 2019 Dec;31(12):e12810. doi: 10.1111/jne.12810. J Neuroendocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31715027 Free PMC article.
-
Undernutrition reduces kisspeptin and neurokinin B expression in castrated male sheep.Reprod Fertil. 2020 Oct 31;1(1):1-13. doi: 10.1530/RAF-20-0025. eCollection 2020 Jul. Reprod Fertil. 2020. PMID: 35128420 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between kisspeptin and neurokinin B in the control of GnRH secretion in the female rat.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jan;300(1):E202-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00517.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21045176 Free PMC article.
-
Role for Kisspeptin and Neurokinin B in Regulation of Luteinizing Hormone and Testosterone Secretion in the Fetal Sheep.Endocrinology. 2020 Apr 1;161(4):bqaa013. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa013. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32005991 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroendocrine control by kisspeptins: role in metabolic regulation of fertility.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011 Sep 13;8(1):40-53. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.147. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21912400 Review.
References
-
- Seminara SB, Messager S, Chatzidaki EE, Thresher RR, Acierno Jr JS, Shagoury JK, Bo-Abbas Y, Kuohung W, Schwinof KM, Hendrick AG, Zahn D, Dixon J, Kaiser UB, Slaugenhaupt SA, Gusella JF, O'Rahilly S, Carlton MB, Crowley Jr WF, Aparicio SA, Colledge WH 2003 The GPR54 gene as a regulator of puberty. N Engl J Med 349:1614–1627 - PubMed
-
- Smith JT 2009 Sex steroid control of hypothalamic Kiss 1 expression in sheep and rodents: comparative aspects. Peptides 30:94–102 - PubMed

