Altered differentiation and proliferation of prostate epithelium in mice lacking the androgen receptor cofactor p44/WDR77
- PMID: 20519372
- PMCID: PMC2940529
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1080
Altered differentiation and proliferation of prostate epithelium in mice lacking the androgen receptor cofactor p44/WDR77
Abstract
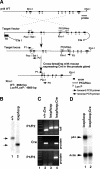
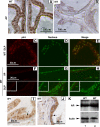
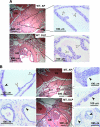
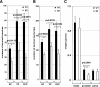
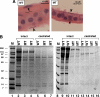
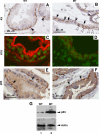
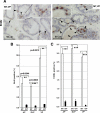
Although it has been observed that various cofactors modulate activity of the androgen receptor (AR), the specific relationship between AR cofactors and prostate development and functions has not been well studied. To determine whether AR cofactor p44/WDR77 is important in prostate growth and development, we examined prostate architecture in p44/WDR77-null mice and wild-type (WT) littermates. Prostate glands from p44/WDR77-deficient animals were not only smaller than those from WT mice but also had fewer branches and terminal duct tips and were deficient in production of secretory proteins. The p44/WDR77-null prostate tissue was less differentiated and hyperproliferative relative to WT littermates. In addition, the altered expression of androgen-regulated genes was observed in the p44/WDR77-null prostate. Thus, these results suggest that the AR cofactor p44/WDR77 plays important roles in prostate growth and differentiation by modulating AR-target gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Cunha GR, Chung LW 1981 Stromal-epithelial interactions–I. Induction of prostatic phenotype in urothelium of testicular feminized (Tfm/y) mice. J Steroid Biochem 14:1317–1324 - PubMed
-
- Donjacour AA, Cunha GR 1993 Assessment of prostatic protein secretion in tissue recombinants made of urogenital sinus mesenchyme and urothelium from normal or androgen-insensitive mice. Endocrinology 132:2342–2350 - PubMed
-
- Rittenhouse HG, Finlay JA, Mikolajczyk SD, Partin AW 1998 Human Kallikrein 2 (hK2) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA): two closely related, but distinct, kallikreins in the prostate. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 35:275–368 - PubMed
-
- Isaacs JT, Coffey DS 1989 Etiology and disease process of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate Suppl 2:33–50 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

