Evaluation of multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis for typing a polyclonal hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus population in an area where such infections are endemic
- PMID: 20519480
- PMCID: PMC2916587
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02220-09
Evaluation of multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis for typing a polyclonal hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus population in an area where such infections are endemic
Abstract
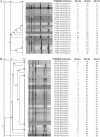
Multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis (MLVA) was performed with 292 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates previously characterized by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, multilocus sequence typing, and staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec typing. Quantitative correspondence analyses showed the best correlation between data when an >or=80% cutoff was applied to MLVA. We confirmed the validity of MLVA for identification of related strains in a polyclonal MRSA population.
Figures
References
-
- Abramson, M. A., and D. J. Sexton. 1999. Nosocomial methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus primary bacteremia: at what costs? Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 20:408-411. - PubMed
-
- Chaberny, I. F., F. Schwab, S. Ziesing, S. Suerbaum, and P. Gastmeier. 2008. Impact of routine surgical ward and intensive care unit admission surveillance cultures on hospital-wide nosocomial methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a university hospital: an interrupted time-series analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 62:1422-1429. - PubMed
-
- Crisóstomo, M. I., H. Westh, A. Tomasz, M. Chung, D. C. Oliveira, and H. de Lencastre. 2001. The evolution of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: similarity of genetic backgrounds in historically early methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates and contemporary epidemic clones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98:9865-9870. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crossley, K., B. Landsman, and D. Zaske. 1979. An outbreak of infections caused by strains of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to methicillin and aminoglycosides. II. Epidemiologic studies. J. Infect. Dis. 139:280-287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

