Aurora kinases A and B are up-regulated by Myc and are essential for maintenance of the malignant state
- PMID: 20519624
- PMCID: PMC2938839
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-251074
Aurora kinases A and B are up-regulated by Myc and are essential for maintenance of the malignant state
Abstract
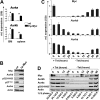
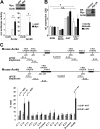
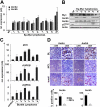
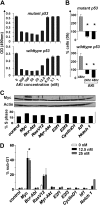
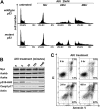
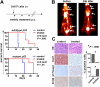
Myc oncoproteins promote continuous cell growth, in part by controlling the transcription of key cell cycle regulators. Here, we report that c-Myc regulates the expression of Aurora A and B kinases (Aurka and Aurkb), and that Aurka and Aurkb transcripts and protein levels are highly elevated in Myc-driven B-cell lymphomas in both mice and humans. The induction of Aurka by Myc is transcriptional and is directly mediated via E-boxes, whereas Aurkb is regulated indirectly. Blocking Aurka/b kinase activity with a selective Aurora kinase inhibitor triggers transient mitotic arrest, polyploidization, and apoptosis of Myc-induced lymphomas. These phenotypes are selectively bypassed by a kinase inhibitor-resistant Aurkb mutant, demonstrating that Aurkb is the primary therapeutic target in the context of Myc. Importantly, apoptosis provoked by Aurk inhibition was p53 independent, suggesting that Aurka/Aurkb inhibitors will show efficacy in treating primary or relapsed malignancies having Myc involvement and/or loss of p53 function.
Figures

References
-
- Boxer LM, Dang CV. Translocations involving c-myc and c-myc function. Oncogene. 2001;20(40):5595–5610. - PubMed
-
- Bernard S, Eilers M. Control of cell proliferation and growth by Myc proteins. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;42:329–342. - PubMed
-
- Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan GI. Suppression of Myc-induced apoptosis in beta cells exposes multiple oncogenic properties of Myc and triggers carcinogenic progression. Cell. 2002;109(3):321–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

