The presence of GAD and IA-2 antibodies in youth with a type 2 diabetes phenotype: results from the TODAY study
- PMID: 20519658
- PMCID: PMC2928346
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0373
The presence of GAD and IA-2 antibodies in youth with a type 2 diabetes phenotype: results from the TODAY study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the frequency of islet cell autoimmunity in youth clinically diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and describe associated clinical and laboratory findings.
Research design and methods: Children (10-17 years) diagnosed with type 2 diabetes were screened for participation in the Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth (TODAY) study. Measurements included GAD-65 and insulinoma-associated protein 2 autoantibodies using the new National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases/National Institutes of Health (NIDDK/NIH) standardized assays, a physical examination, and fasting lipid, C-peptide, and A1C determinations.
Results: Of the 1,206 subjects screened and considered clinically to have type 2 diabetes, 118 (9.8%) were antibody positive; of these, 71 (5.9%) were positive for a single antibody, and 47 were positive (3.9%) for both antibodies. Diabetes autoantibody (DAA) positivity was significantly associated with race (P < 0.0001), with positive subjects more likely to be white (40.7 vs. 19%) (P < 0.0001) and male (51.7 vs. 35.7%) (P = 0.0007). BMI, BMI z score, C-peptide, A1C, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, and blood pressure were significantly different by antibody status. The antibody-positive subjects were less likely to display characteristics clinically associated with type 2 diabetes and a metabolic syndrome phenotype, although the range for BMI z score, blood pressure, fasting C-peptide, and serum lipids overlapped between antibody-positive and antibody-negative subjects.
Conclusions: Obese youth with a clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes may have evidence of islet autoimmunity contributing to insulin deficiency. As a group, patients with DAA have clinical characteristics significantly different from those without DAA. However, without islet autoantibody analysis, these characteristics cannot reliably distinguish between obese young individuals with type 2 diabetes and those with autoimmune diabetes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00081328.
Figures
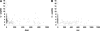
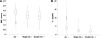
References
-
- Pinhas-Hamiel O, Dolan LM, Daniels SR, Standiford D, Khoury PR, Zeitler P: Increased incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among adolescents. J Pediatr 1996;128(5 Pt 1):608–615 - PubMed
-
- Dabelea D, Pettitt DJ, Jones KL, Arslanian SA: Type 2 diabetes mellitus in minority children and adolescents. An emerging problem. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1999;28:709–729, viii - PubMed
-
- Fagot-Campagna A, Pettitt DJ, Engelgau MM, Burrows NR, Geiss LS, Valdez R, Beckles GL, Saaddine J, Gregg EW, Williamson DF, Narayan KM: Type 2 diabetes among North American children and adolescents: an epidemiologic review and a public health perspective. J Pediatr 2000;136:664–672 - PubMed
-
- Writing Group for the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. JAMA 2007;297:2716–2724 - PubMed
-
- Vehik K, Hamman RF, Lezotte D, Norris JM, Klingensmith G, Bloch C, Rewers M, Dabelea D: Increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes in 0- to 17-year-old Colorado youth. Diabetes Care 2007;30:503–509 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01-DK-61230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR014467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR14467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00043-45/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

