Evolution of percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with diabetes: a report from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-sponsored PTCA (1985-1986) and Dynamic (1997-2006) Registries
- PMID: 20519661
- PMCID: PMC2928347
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0247
Evolution of percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with diabetes: a report from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-sponsored PTCA (1985-1986) and Dynamic (1997-2006) Registries
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the association of successive percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) modalities with balloon angioplasty (BA), bare-metal stent (BMS), drug-eluting stents (DES), and pharmacotherapy over the last 3 decades with outcomes among patients with diabetes in routine clinical practice.
Research design and methods: We examined outcomes in 1,846 patients with diabetes undergoing de novo PCI in the multicenter, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-sponsored 1985-1986 Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) Registry and 1997-2006 Dynamic Registry. Multivariable Cox regression models were used to estimate the adjusted risk of events (death/myocardial infarction [MI], repeat revascularization) over 1 year.
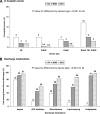
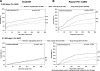
Results: Cumulative event rates for postdischarge (31-365 days) death/MI were 8% by BA, 7% by BMS, and 7% by DES use (P = 0.76) and for repeat revascularization were 19, 13, and 9% (P < 0.001), respectively. Multivariable analysis showed a significantly lower risk of repeat revascularization with DES use when compared with the use of BA (hazard ratio [HR] 0.41 [95% CI 0.29-0.58]) and BMS (HR 0.55 [95% CI 0.39-0.76]). After further adjustment for discharge medications, the lower risk for death/MI was not statistically significant for DES when compared with BA.
Conclusions: In patients with diabetes undergoing PCI, the use of DES is associated with a reduced need for repeat revascularization when compared with BA or BMS use. The associated death/MI benefit observed with the DES versus the BA group may well be due to greater use of pharmacotherapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00005677.
Figures

References
-
- Venkitachalam L, Kip KE, Selzer F, Wilensky RL, Slater J, Mulukutla SR, Marroquin OC, Block PC, Williams DO, Kelsey SF: Investigators of NHLBI-Sponsored 1985–1986 PTCA and 1997–2006 Dynamic Registries. Twenty-year evolution of percutaneous coronary intervention and its impact on clinical outcomes: a report from the NHLBI-sponsored, multicenter 1985–86 PTCA and 1997–2006 Dynamic Registries. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2009;2:6–13 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stettler C, Wandel S, Allemann S, Kastrati A, Morice MC, Schömig A, Pfisterer ME, Stone GW, Leon MB, de Lezo JS, Goy JJ, Park SJ, Sabaté M, Suttorp MJ, Kelbaek H, Spaulding C, Menichelli M, Vermeersch P, Dirksen MT, Cervinka P, Petronio AS, Nordmann AJ, Diem P, Meier B, Zwahlen M, Reichenbach S, Trelle S, Windecker S, Jüni P: Outcomes associated with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: a collaborative network meta-analysis. Lancet 2007;370:937–948 - PubMed
-
- Stein B, Weintraub WS, Gebhart SP, Cohen-Bernstein CL, Grosswald R, Liberman HA, Douglas JS, Jr, Morris DC, King SB, 3rd: Influence of diabetes mellitus on early and late outcome after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1995;91:979–989 - PubMed
-
- Abizaid A, Kornowski R, Mintz GS, Hong MK, Abizaid AS, Mehran R, Pichard AD, Kent KM, Satler LF, Wu H, Popma JJ, Leon MB: The influence of diabetes mellitus on acute and late clinical outcomes following coronary stent implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;32:584–589 - PubMed
-
- Spaulding C, Daemen J, Boersma E, Cutlip DE, Serruys PW: A pooled analysis of data comparing sirolimus-eluting stents with bare-metal stents. N Engl J Med 2007;356:989–997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

