New therapeutic strategies targeting transmembrane signal transduction in the immune system
- PMID: 20519929
- PMCID: PMC2900623
- DOI: 10.4161/cam.4.2.10746
New therapeutic strategies targeting transmembrane signal transduction in the immune system
Abstract
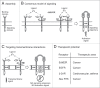
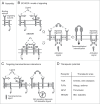
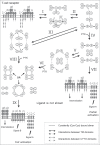
Single-chain receptors and multi-chain immune recognition receptors (SRs and MIRRs, respectively) represent families of structurally related but functionally different surface receptors expressed on different cells. In contrast to SRs, a distinctive and common structural characteristic of MIRR family members is that the extracellular recognition domains and intracellular signaling domains are located on separate subunits. How extracellular ligand binding triggers MIRRs and initiates intracellular signal transduction processes is not clear. A novel model of immune signaling, the Signaling Chain HOmoOLigomerization (SCHOOL) model, suggests that the homooligomerization of receptor intracellular signaling domains represents a necessary and sufficient condition for receptor triggering. In this review, I demonstrate striking similarities between a consensus model of SR signaling and the SCHOOL model of MIRR signaling and show how these models, together with the lessons learned from viral pathogenesis, provide a molecular basis for novel pharmacological approaches targeting inter- and intrareceptor transmembrane interactions as universal therapeutic targets for a diverse variety of immune and other disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Rudd CE. Disabled receptor signaling and new primary immunodeficiency disorders. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1874–1877. - PubMed
-
- Sigalov AB, editor. Multichain Immune Recognition Receptor Signaling: From Spatiotemporal Organization to Human Disease. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2008. - PubMed
-
- Keegan AD, Paul WE. Multichain immune recognition receptors: similarities in structure and signaling pathways. Immunol Today. 1992;13:63–68. - PubMed
-
- Sigalov AB. Immune cell signaling: a novel mechanistic model reveals new therapeutic targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:518–524. - PubMed
-
- Heldin CH. Dimerization of cell surface receptors in signal transduction. Cell. 1995;80:213–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
