Ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) CDK inhibitors
- PMID: 20519948
- PMCID: PMC3319752
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.12.11988
Ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) CDK inhibitors
Abstract
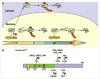
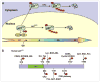
The expression levels of the p21(Cip1) family CDK inhibitors (CKIs), p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2), play a pivotal role in the precise regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity, which is instrumental to proper cell cycle progression. The stabilities of p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) are all tightly and differentially regulated by ubiquitylation and proteasome-mediated degradation during various stages of the cell cycle, either in steady state or in response to extracellular stimuli, which often elicit site-specific phosphorylation of CKIs triggering their degradation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CDK inhibitors, p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1), participate in cell cycle exit of mammalian cardiomyocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 17;443(3):1105-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.109. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24380855
-
Expression of p21(Wafl/Cip1), p57(Kip2) and HER2/neu in patients with gallbladder cancer.Anticancer Res. 2007 May-Jun;27(3B):1679-84. Anticancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17595796
-
CDK inhibitors selectively diminish cell cycle controlled activation of the histone H4 gene promoter by p220NPAT and HiNF-P.J Cell Physiol. 2009 May;219(2):438-48. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21687. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19170105 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple roles of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory protein p57(KIP2) in cerebral cortical neurogenesis.Dev Neurobiol. 2012 Jun;72(6):821-42. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20999. Dev Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22076965 Review.
-
Regulation of p27Kip1 and p57Kip2 Functions by Natural Polyphenols.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 13;10(9):1316. doi: 10.3390/biom10091316. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32933137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitization of lung cancer cells to cisplatin by β-elemene is mediated through blockade of cell cycle progression: antitumor efficacies of β-elemene and its synthetic analogs.Med Oncol. 2013 Mar;30(1):488. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0488-9. Epub 2013 Feb 9. Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23397083
-
Deubiquitinase PSMD7 regulates cell fate and is associated with disease progression in breast cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Sep 15;12(9):5433-5448. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33042429 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of ciliogenesis suppression in dividing cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Mar;74(5):881-890. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2369-9. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27669693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial hepatectomy in rats results in immediate down-regulation of p27Kip1 in residual liver tissue by transcriptional and post-translational processes.Front Physiol. 2013 Jun 13;4:139. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00139. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23781207 Free PMC article.
-
ATM-Mediated translocation of RanBPM regulates DNA damage response by stabilizing p21 in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Feb;47(1):245-258. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00866-x. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 37676377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson PK, Eldridge AG, Freed E, Furstenthal L, Hsu JY, Kaiser BK, et al. The lore of the RINGs: substrate recognition and catalysis by ubiquitin ligases. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:429–39. - PubMed
-
- Hatakeyama S, Yada M, Matsumoto M, Ishida N, Nakayama KI. U box proteins as a new family of ubiquitin-protein ligases. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:33111–20. - PubMed
-
- Boname JM, Stevenson PG. MHC class I ubiquitination by a viral PHD/LAP finger protein. Immunity. 2001;15:627–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
