Inter-alpha inhibitor protein administration improves survival from neonatal sepsis in mice
- PMID: 20520583
- PMCID: PMC2928396
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181e9fdf0
Inter-alpha inhibitor protein administration improves survival from neonatal sepsis in mice
Abstract
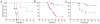
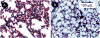
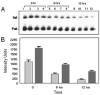
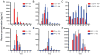
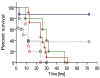
Inter-alpha inhibitor proteins (IaIp) are serine proteases inhibitors that modulate endogenous protease activity and have been shown to improve survival in adult models of sepsis. We evaluated the effect of IaIp on survival and systemic responses to sepsis in neonatal mice. Sepsis was induced in 2-d-old mice with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), Escherichia coli, and group B Streptococci. Sepsis was associated with 75% mortality. IaIp, given by i.p. administration at doses between 15 and 45 mg/kg from 1 to 6 h after the onset of sepsis, improved survival to approximately 90% (p = 0.0159) in both LPS-induced sepsis and with live bacterial infections. The greatest effect was on reversal of hemorrhagic pneumonitis. The effects were dose and time dependent. Systemic cytokine profile and tissue histology were examined. Survival was compared in IL-10 knock out animals. Systemic cytokine levels including TNF-[alpha] and IL-10 were increased after induction of sepsis and modulated significantly after IaIp administration. Because the effect of IaIp was still demonstrable in IL-10 deficient mice, we conclude the beneficial effects of IaIp is because of suppression of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-[alpha] rather than augmentation of IL-10. IaIp may offer significant benefits as a therapeutic
Figures
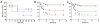
Similar articles
-
Exogenous inter-α inhibitor proteins prevent cell death and improve ischemic stroke outcomes in mice.J Clin Invest. 2021 Sep 1;131(17):e144898. doi: 10.1172/JCI144898. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34580244 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-alpha inhibitor proteins in infants and decreased levels in neonatal sepsis.J Pediatr. 2003 Jul;143(1):11-5. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(03)00190-2. J Pediatr. 2003. PMID: 12915817
-
Inter-α inhibitor protein and its associated glycosaminoglycans protect against histone-induced injury.Blood. 2015 Apr 2;125(14):2286-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-06-582759. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25631771 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal sepsis: an old problem with new insights.Virulence. 2014 Jan 1;5(1):170-8. doi: 10.4161/viru.26906. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Virulence. 2014. PMID: 24185532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neonatal infectious diseases: evaluation of neonatal sepsis.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2013 Apr;60(2):367-89. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2012.12.003. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2013. PMID: 23481106 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inter-alpha inhibitor proteins attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced blood-brain barrier disruption and downregulate circulating interleukin 6 in mice.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 May;40(5):1090-1102. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19859465. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 31234704 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme K activates protease-activated receptor-1.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21484. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021484. Epub 2011 Jun 30. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21760880 Free PMC article.
-
Revelation of Proteomic Indicators for Colorectal Cancer in Initial Stages of Development.Molecules. 2020 Jan 31;25(3):619. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030619. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32023884 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous inter-α inhibitor proteins prevent cell death and improve ischemic stroke outcomes in mice.J Clin Invest. 2021 Sep 1;131(17):e144898. doi: 10.1172/JCI144898. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34580244 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia reduces inter-alpha inhibitor proteins in the brain of the ovine fetus.Dev Neurobiol. 2017 Jun;77(6):726-737. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22451. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Dev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27618403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyde TB, Hilger TM, Reingold A, Farley MM, O’Brien KL, Schuchat A. Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) of the Emerging Infections Program Network. Trends in incidence and antimicrobial resistance of early-onset sepsis; Population-based surveillance in San Francisco and Atlanta. Pediatrics. 2002;110:690–695. - PubMed
-
- Puopolo KM, Madoff LC, Eichenwald EC. Early-onset group B streptococcal disease in the era of maternal screening. Pediatrics. 2005;115:1240–1246. - PubMed
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Higgins RD, Fanaroff AA, Duara S, Goldberg R, Laptook AR, Walsh M, Oh W, Hale E. Very low birth weight preterm infants with early onset neonatal sepsis: The predominance of gram-negative infections continues in the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network, 2002–2003. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:635–639. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002;420:885–891. - PubMed
-
- Jochum M, Gippner-Steppert C, Machleidt W, Fritz H. The role of phagocyte proteases and proteinase inhibitors in multiple organ failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;150:S123–S130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

