Enhanced expression of lmb gene encoding laminin-binding protein in Streptococcus agalactiae strains harboring IS1548 in scpB-lmb intergenic region
- PMID: 20520730
- PMCID: PMC2875397
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010794
Enhanced expression of lmb gene encoding laminin-binding protein in Streptococcus agalactiae strains harboring IS1548 in scpB-lmb intergenic region
Abstract
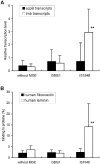
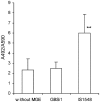
Group B streptococcus (GBS) is the main cause of neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Bacterial surface proteins play a major role in GBS binding to and invasion of different host surfaces. The scpB and lmb genes, coding for fibronectin-binding and laminin-binding surface proteins, are present in almost all human GBS isolates. The scpB-lmb intergenic region is a hot spot for integration of two mobile genetic elements (MGEs): the insertion element IS1548 or the group II intron GBSi1. We studied the structure of scpB-lmb intergenic region in 111 GBS isolates belonging to the intraspecies major clonal complexes (CCs). IS1548 was mostly found (72.2%) in CC19 serotype III strains recovered more specifically (92.3%) from neonatal meningitis. GBSi1 was principally found (70.6%) in CC17 strains, mostly (94.4%) of serotype III, but also (15.7%) in CC19 strains, mostly (87.5%) of serotype II. No MGE was found in most strains of the other CCs (76.0%), notably CC23, CC10 and CC1. Twenty-six strains representing these three genetic configurations were selected to investigate the transcription and expression levels of scpB and lmb genes. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that lmb transcripts were 5.0- to 9.6-fold higher in the group of strains with IS1548 than in the other two groups of strains (P<0.001). Accordingly, the binding ability to laminin was 3.8- to 6.6-fold higher in these strains (P< or =0.001). Moreover, Lmb amount expressed on the cell surface was 2.4- to 2.7-fold greater in these strains (P<0.001). By contrast, scpB transcript levels and fibronectin binding ability were similar in the three groups of strains. Deletion of the IS1548 sequence between scpB and lmb genes in a CC19 serotype III GBS strain substantially reduced the transcription of lmb gene (13.5-fold), the binding ability to laminin (6.2-fold), and the expression of Lmb protein (5.0-fold). These data highlight the importance of MGEs in bacterial virulence and demonstrate the up-regulation of lmb gene by IS1548; the increased lmb gene expression observed in CC19 serotype III strains with IS1548 may play a role in their ability to cause neonatal meningitis and endocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Farley MM. Group B streptococcal disease in nonpregnant adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:556–561. - PubMed
-
- Bisharat N, Jones N, Marchaim D, Block C, Harding RM, et al. Population structure of group B streptococcus from a low-incidence region for invasive neonatal disease. Microbiology. 2005;151:1875–1881. - PubMed
-
- Davies HD, Jones N, Whittam TS, Elsayedr N, Bisharat N, et al. Multilocus sequence typing of serotype III group B streptococcus and correlation with pathogenic potential. J Infect Dis. 2005;189:1097–1102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

