Effects of MDM2, MDM4 and TP53 codon 72 polymorphisms on cancer risk in a cohort study of carriers of TP53 germline mutations
- PMID: 20520810
- PMCID: PMC2877078
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010813
Effects of MDM2, MDM4 and TP53 codon 72 polymorphisms on cancer risk in a cohort study of carriers of TP53 germline mutations
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have shown that MDM2 SNP309 and p53 codon 72 have modifier effects on germline P53 mutations, but those studies relied on case-only studies with small sample sizes. The impact of MDM4 polymorphism on tumor onset in germline mutation carriers has not previously been studied.
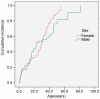
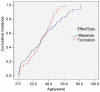
Methodology/principal findings: We analyzed 213 p53 germline mutation carriers including 168(78.9%) affected with cancer and 174 who had genotypic data. We analyzed time to first cancer using Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards methods, comparing risks according to polymorphism genotypes. For MDM2 SNP309, a significant difference of 9.0 years in the average age of cancer diagnosis was observed between GG/GT and TT carriers (18.6 versus 27.6 years, P = 0.0087). The hazards ratio was 1.58 (P = 0.03) comparing risks among individuals with GG/GT to risk among TT, but this effect was only significant in females (HR = 1.60, P = 0.02). Compared to other genotypes, P53 codon 72 PP homozygotes had a 2.24 times (P = 0.03) higher rate for time to develop cancer. We observed a multiplicative joint effect of MDM2 and p53 codon72 polymorphism on risk. The MDM4 polymorphism had no significant effects.
Conclusions/significance: Our results suggest that the MDM2 SNP309 G allele is associated with cancer risk in p53 germline mutation carriers and accelerates time to cancer onset with a pronounced effect in females. A multiplicative joint effect exists between the MDM2 SNP309 G allele and the p53 codon 72 G allele in the risk of cancer development. Our results further define cancer risk in carriers of germline p53 mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms TP53 R72P and MDM2 SNP309, and p53 expression on survival of breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(6):R89. doi: 10.1186/bcr2460. Epub 2009 Dec 18. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 20021639 Free PMC article.
-
Joint effects of germ-line TP53 mutation, MDM2 SNP309, and gender on cancer risk in family studies of Li-Fraumeni syndrome.Hum Genet. 2011 Jun;129(6):663-73. doi: 10.1007/s00439-011-0957-1. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21305319 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the germline TP53 R72P and MDM2 SNP309 variants with breast cancer survival in specific breast tumor subgroups.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130(2):599-608. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1615-y. Epub 2011 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21667122
-
The Mdm network and its regulation of p53 activities: a rheostat of cancer risk.Hum Mutat. 2014 Jun;35(6):728-37. doi: 10.1002/humu.22524. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Hum Mutat. 2014. PMID: 24488925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case-control study on the SNP309T → G and 40-bp Del1518 of the MDM2 gene and a systematic review for MDM2 polymorphisms in the patients with breast cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Dec;34(12):e23529. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23529. Epub 2020 Sep 20. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32951271 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lymph Node Metastasis From Gastroesophageal Cancer Successfully Treated by Nivolumab: A Case Report of a Young Patient.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 16;9:1375. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01375. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31921639 Free PMC article.
-
Li-fraumeni syndrome.Genes Cancer. 2011 Apr;2(4):475-84. doi: 10.1177/1947601911413466. Genes Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21779515 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of TP53 Pro72Arg and MDM2 SNP285-SNP309 polymorphisms in an Italian cohort of LFS suggestive patients lacking identifiable TP53 germline mutations.Fam Cancer. 2016 Oct;15(4):635-43. doi: 10.1007/s10689-016-9895-3. Fam Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26956143
-
The codon 72 polymorphism of p53 regulates interaction with NF-{kappa}B and transactivation of genes involved in immunity and inflammation.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Mar;31(6):1201-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01136-10. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21245379 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into TP53 mutation (p. Arg267Trp) and its connection to Choroid Plexus Carcinomas and Li-Fraumeni Syndrome.Genes Genomics. 2024 Aug;46(8):941-953. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01531-9. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38896352
References
-
- Jin S, Levine AJ. The p53 functional circuit. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:4139–4140. - PubMed
-
- Malkin D. p53 and the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1198:197–213. - PubMed
-
- Garber JE, Goldstein AM, Kantor AF, Dreyfus MG, Fraumeni JF, Jr, et al. Follow-up study of twenty-four families with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cancer Res. 1991;51:6094–6097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

