Childhood adversities are associated with shorter telomere length at adult age both in individuals with an anxiety disorder and controls
- PMID: 20520834
- PMCID: PMC2876034
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010826
Childhood adversities are associated with shorter telomere length at adult age both in individuals with an anxiety disorder and controls
Abstract
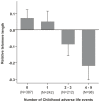
Accelerated leukocyte telomere shortening has been previously associated to self-perceived stress and psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and mood disorders. We set out to investigate whether telomere length is affected in patients with anxiety disorders in which stress is a known risk factor. We also studied the effects of childhood and recent psychological distress on telomere length. We utilized samples from the nationally representative population-based Health 2000 Survey that was carried out between 2000-2001 in Finland to assess major public health problems and their determinants. We measured the relative telomere length of the peripheral blood cells by quantitative real-time PCR from 321 individuals with DSM-IV anxiety disorder or subthreshold diagnosis and 653 matched controls aged 30-87 years, who all had undergone the Composite International Diagnostic Interview. While telomere length did not differ significantly between cases and controls in the entire cohort, the older half of the anxiety disorder patients (48-87 years) exhibited significantly shorter telomeres than healthy controls of the same age (P = 0.013). Interestingly, shorter telomere length was also associated with a greater number of reported childhood adverse life events, among both the anxiety disorder cases and controls (P = 0.005). Childhood chronic or serious illness was the most significantly associated single event affecting telomere length at the adult age (P = 0.004). Self-reported current psychological distress did not affect telomere length. Our results suggest that childhood stress might lead to accelerated telomere shortening seen at the adult age. This finding has potentially important implications supporting the view that childhood adversities might have a considerable impact on well being later in life.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Childhood adversities are associated with shorter leukocyte telomere length at adult age in a population-based study.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2021 Aug;130:105276. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2021.105276. Epub 2021 May 21. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2021. PMID: 34051657
-
Association between anxiety but not depressive disorders and leukocyte telomere length after 2 years of follow-up in a population-based sample.Psychol Med. 2013 Apr;43(4):689-97. doi: 10.1017/S0033291712001766. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Psychol Med. 2013. PMID: 22877856
-
Early and recent psychosocial stress and telomere length in older adults.Int Psychogeriatr. 2016 Mar;28(3):405-13. doi: 10.1017/S1041610215001155. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Int Psychogeriatr. 2016. PMID: 26265356
-
Telomere Shortening and Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review.Cells. 2021 Jun 7;10(6):1423. doi: 10.3390/cells10061423. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34200513 Free PMC article.
-
[Associations between depression, anxiety and telomere length in a large Dutch psychiatric cohort study].Tijdschr Psychiatr. 2017;59(6):350-359. Tijdschr Psychiatr. 2017. PMID: 28613367 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Stress and telomere shortening among central Indian conservation refugees.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 3;112(9):E928-36. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411902112. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25730846 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte telomere length in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034948. Epub 2012 Apr 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22493726 Free PMC article.
-
No association between mean telomere length and life stress observed in a 30 year birth cohort.PLoS One. 2014 May 9;9(5):e97102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097102. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24816913 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the contributions of childhood maltreatment subtypes and depression case-control status on telomere length reveals a specific role of physical neglect.J Affect Disord. 2017 Apr 15;213:16-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.01.031. Epub 2017 Feb 3. J Affect Disord. 2017. PMID: 28187293 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting cardiovascular morbidity and mortality with SCORE2 (OP) and Framingham risk estimates in combination with indicators of biological ageing.Age Ageing. 2025 Mar 28;54(4):afaf075. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afaf075. Age Ageing. 2025. PMID: 40178198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blasco MA. Telomeres and human disease: ageing, cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:611–622. - PubMed
-
- von Zglinicki T. Oxidative stress shortens telomeres. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002;27:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff C, Graakjaer J, Petersen HC, Hjelmborg JB, Vaupel JW, et al. The heritability of telomere length among the elderly and oldest-old. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2005;8:433–439. - PubMed

