Prognostic significance of mucin and p53 expression in stage IB non-small cell lung cancer: a laboratory companion study to CALGB 9633
- PMID: 20521348
- PMCID: PMC3505667
- DOI: 10.1097/jto.0b013e3181d89f95
Prognostic significance of mucin and p53 expression in stage IB non-small cell lung cancer: a laboratory companion study to CALGB 9633
Abstract
Introduction: Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9633 was a phase III trial that randomized patients with stage IB non-small cell lung cancer to observation or four cycles of carboplatin and paclitaxel. A statistically significant effect in favor of adjuvant chemotherapy was seen for disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in the subgroup of patients with tumors > or =4 cm. A laboratory companion study was conducted to see whether molecular and clinical factors could provide additional prognostic information.
Methods: Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded blocks were obtained for 250 of the 344 patients enrolled. Immunohistochemical staining for bcl-2, p53, blood group antigen A, and mucin was correlated with DFS and OS.
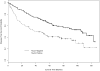
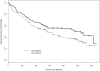
Results: The prevalence of the markers was bcl-2, 17%; p53, 47%; blood group antigen A, 25%; and mucin, 45%. Univariate analysis for DFS showed a statistically significant effect for the presence of mucin (p = 0.0005) and p53 (p = 0.05) and for OS showed a significant effect for mucin (p = 0.0005). In the multivariate Cox model, there was a statistically significant association between shorter DFS and presence of mucin (p = 0.002; hazard ratio [HR] 2.05) and p53 (p = 0.003; HR 1.95) and between shorter OS and presence of mucin (p = 0.004; HR 2.03) and p53 (p = 0.0005; HR 2.30). Of the clinical factors, male gender and larger tumor volume were also significant adverse prognostic factors (p 0.05).
Conclusions: A statistically significant association between shorter DFS and OS was seen for the patients with p53 protein expression, mucin expression, male gender, and larger tumors in this cohort of patients with stage IB non-small cell lung cancer treated on Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9633.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer Statistics 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global cancer rates could increase 50% to 15 million by 2020 [WHO Web site] Apr 3, 2003. [Accessed Jan 18, 2010]. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2003/pr27/en.
-
- The International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial Collaborative Group. Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:351–360. - PubMed
-
- Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, et al. Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs. observation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;52:2589–2597. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Rosell R, De Lena M, et al. Adjuvant vinorelbine plus cisplatin versus observation in patients with completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer (Adjuvant Navelbine International Trialist Association [ANITA]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:719–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA33601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA026806/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA074811/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031983/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047555/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077406/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA086726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045564/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA41287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA008025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA007968/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA059518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004326/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA041287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA016450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA060138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA08025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012046/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA003927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

