Inhibition of DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases induces bone marrow-derived multipotent adult progenitor cells to differentiate into endothelial cells
- PMID: 20521387
- PMCID: PMC5702555
Inhibition of DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases induces bone marrow-derived multipotent adult progenitor cells to differentiate into endothelial cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: Inhibition of DNA Methyltransferases and Histone Deacetylases Induces Bone Marrow-derived Multipotent Adult Progenitor Cells to Differentiate into Endothelial Cells.Ethn Dis. 2018 Oct 18;28(4):586. doi: 10.18865/ed.28.4.586. Ethn Dis. 2018. PMID: 30405305 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Endothelial dysfunction plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Bone marrow-derived multipotent adult progenitor cells (MAPC) have the potential to differentiate, at the single cell level, toward the three embryonic germ layers and may be the progenitors of the other tissue-specific stem cells. However, molecular mechanisms of endothelial differentiation from MAPC have not been defined. The importance of epigenetic changes such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation in gene regulatory networks during embryonic stem cell (ESC) differentiation has been documented. We postulated that endothelial cell (EC) differentiation from MAPC could be enhanced by inhibiting DNA methylation and histone deacetylation, reversing the repression of genes that specify EC fate.
Methods: MAPCs were derived from rat bone marrow and differentiated into EC by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) treatment in the presence or absence of the specific DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitor 5'-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (aza-dC) and the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA). Expression of the endothelial marker genes was assessed by real time quantitative PCR and angiogenic potential of the differentiated EC was assessed by analysis of vascular network formation on fibronectin.
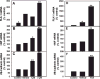
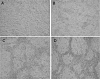
Results: Both aza-dC and TSA induced at least a three-fold increase in the expression of the EC marker genes VE-cadherin, vWF, and Flk1. This increase was also observed in the presence of the EC differentiation inducer VEGF, suggesting that factors other than VEGF mediate the response to the epigenetic agents. Both DNMT and HDAC inhibition stimulated vascular network formation.
Conclusion: Epigenetic therapy holds a potential in inducing self-repair, vascular tissue regeneration, controlling angiogenesis and endothelial dysfunction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA methyltransferase inhibition induces mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation into endothelial cells.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Jan 15;316(2):172-80. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.08.011. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 19715692 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dynamic DNA methylation and histone acetylation on cPouV expression in differentiation of chick embryonic germ cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Oct 15;22(20):2725-35. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0046. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23750509 Free PMC article.
-
DNMT and HDAC inhibitors modulate MMP-9-dependent H3 N-terminal tail proteolysis and osteoclastogenesis.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019 Apr 16;12(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13072-019-0270-0. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019. PMID: 30992059 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of histone deacetylase inhibitors and DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in the treatment of human cancer cells.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003 May;3(3):187-99. doi: 10.2174/1568011033482440. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003. PMID: 12769777 Review.
-
Role of epigenetics in liver-specific gene transcription, hepatocyte differentiation and stem cell reprogrammation.J Hepatol. 2009 Jul;51(1):187-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.009. Epub 2009 Apr 2. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19457566 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic valproate treatment enhances postischemic angiogenesis and promotes functional recovery in a rat model of ischemic stroke.Stroke. 2012 Sep;43(9):2430-6. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.652545. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Stroke. 2012. PMID: 22811460 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of shear stress on differentiation of stem cells into endothelial cells.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Jul 26;13(7):894-913. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.894. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34367483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of HDAC1 is involved in the cardiomyocyte differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells in a myocardial microenvironment.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 1;9(4):e93222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093222. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24690943 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) and Atherosclerosis: A Mechanistic and Pharmacological Review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 12;8:581015. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.581015. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33282862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoglin is a novel endothelial cell specification gene.Stem Cell Res. 2012 Jan;8(1):85-96. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2011.08.006. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Stem Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22099023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Landmesser U, Hornig B, Drexler H. Endothelial function: a critical determinant in atherosclerosis? Circulation. 2004;109(21 Suppl 1):II27–II33. - PubMed
-
- Mints M, Jansson M, Sadeghi B, et al. Endometrial endothelial cells are derived from donor stem cells in a bone marrow transplant recipient. Hum Reprod. 2008;23(1):139–143. - PubMed
-
- Grove JE, Bruscia E, Krause DS. Plasticity of bone marrow-derived stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):487–500. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
