Applying the epidemiologic problem oriented approach (EPOA) methodology in developing a knowledge base for the modeling of HIV/AIDS
- PMID: 20521410
- PMCID: PMC3124961
Applying the epidemiologic problem oriented approach (EPOA) methodology in developing a knowledge base for the modeling of HIV/AIDS
Abstract
Introduction: In the epidemiologic modeling of diseases, the epidemiologic problem oriented approach (EPOA) methodology facilitates the development of systematic and structured knowledge bases, which are crucial for development of models. A detailed understanding of the epidemiology of a given disease provides the essential framework for model development and enables the laying out of the comprehensive and fundamental structures for the models.
Objective: To develop such a knowledge base for developing HIV/AIDS models.
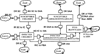
Methods: The EPOA methodology was utilized to develop the knowledge base for HIV/AIDS; it is composed of six pillars within two triads: the Problem Identification/Characterization and the Problem Management/Solution/Mitigation Triads, interlinked by the diagnostic procedure.
Results: Using information from various sources, the triads are decomposed into their respective pillar variables and parameters. The agent pillar identifies the causative agent (HIV) and its characteristics. The host pillar identifies and characterizes the host (human). The environment pillar characterizes the physical, biological and socioeconomic environments for both the host and agent. The therapeutics/treatment pillar considers the treatment options for HIV/AIDS. The prevention/control pillar considers prevention and control measures. The health maintenance/health promotion pillar considers measures for the health maintenance of the population.
Conclusion: Models for HIV/AIDS can be conceptual, in vivo or in vitro, systems analysis, mathematical, or computational just to name a few. The knowledge base developed using the EPOA methodology provides a well-organized structured source of information, which is used in the variable and parameter estimations as well as analysis (biological, mathematical, statistical and computer simulations), which are crucial in epidemiologic modeling of HIV/AIDS. EPOA methodology has become an important tool in the development of models that can enlighten decision making in public health.
Figures

References
-
- Habtemariam T, Yu P, Oryang D, et al. Modelling viral and CD4 cellular opulation dynamics in HIV: approaches to evaluate intervention strategies. Cell Mol Biol. 2001;47(7):1201–1208. - PubMed
-
- Wai-Yuan T, Hulin W, editors. Deterministic and Stochastic Models of AIDS Epidemics and HIV Infections with Intervention. Hackensack, NJ: World Scientific Publishing Company; 2008.
-
- Yu P, Habtemariam T, Oryang D, Nganwa D, Robnett V, Ayanwale L. Modeling the dynamics of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection under chemotherapy intervention. Adv Syst Sci Appl. 1997;2:255–260.
-
- Diaz T, Chu SY, Buehler JW, et al. Socioeconomic differences among people with AIDS: results from a multistate surveillance project. Am J Prev Med. 1994;10(4):217–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
