Relationships between polybrominated diphenyl ether concentrations in house dust and serum
- PMID: 20521814
- PMCID: PMC2917910
- DOI: 10.1021/es100697q
Relationships between polybrominated diphenyl ether concentrations in house dust and serum
Abstract
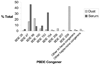
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) have been measured in the home environment and in humans, but studies linking environmental levels to body burdens are limited. This study examines the relationship between PBDE concentrations in house dust and serum from adults residing in these homes. We measured PBDE concentrations in house dust from 50 homes and in serum of male-female couples from 12 of the homes. Detection rates, dust-serum, and within-matrix correlations varied by PBDE congener. There was a strong correlation (r = 0.65-0.89, p < 0.05) between dust and serum concentrations of several predominant PBDE congeners (BDE 47, 99, and 100). Dust and serum levels of BDE 153 were not correlated (r < 0.01). The correlation of dust and serum levels of BDE 209 could not be evaluated due to low detection rates of BDE 209 in serum. Serum concentrations of the sum of BDE 47, 99, and 100 were also strongly correlated within couples (r = 0.85, p = 0.0005). This study provides evidence that house dust is a primary exposure pathway of PBDEs and supports the use of dust PBDE concentrations as a marker for exposure to PBDE congeners other than BDE 153.
Figures

Comment in
-
Fluid assets and liabilities.Environ Sci Technol. 2010 Jul 15;44(14):5319. doi: 10.1021/es1020179. Environ Sci Technol. 2010. PMID: 20707010 No abstract available.
References
-
- ATSDR. Toxicological profile for polybrominated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBBs and PBDEs) Atlanta, GA: Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry; 2004. - PubMed
-
- WHO. World Health Organization, European Environment and Health Information System; 2007. Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Human Milk; Fact Sheet No. 4.3, Code: RPG4_Food_Ex2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

