Microvolt T-wave alternans during Holter monitoring in children and adolescents
- PMID: 20522054
- PMCID: PMC6932606
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2010.00354.x
Microvolt T-wave alternans during Holter monitoring in children and adolescents
Abstract
Background: Time-domain microvolt T-wave alternans (TWA) has been described as a noninvasive marker of sudden cardiac death in adults. The incidence of TWA in pediatric populations has not been defined well. The aim of the study was to determine peculiarities of TWA in children.
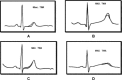
Methods: We examined 68 healthy patients-newborns (20) and children in age group of 7-17 years (48)-and 85 pediatric patients: ventricular premature beats-65; dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMP)-2; long QT syndrome (LQTS)-10; Brugada syndrome (BrS)-5, catecholaminergic ventricular tachycardia (CVT)-3. All underwent Holter monitoring (HM) with definition of the peak value of TWA by modified moving average method.
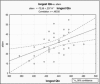
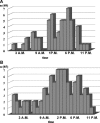
Results: In healthy newborns, TWA was 32 +/- 8 (12-55) microV (HR 123-156 bmp). In healthy children (7-17 years) it was 30 +/- 11 (10-l 55) microV, (HR 64-132 bmp) without any differences between boys and girls. In all group of patients, TWA were significantly higher (P < 0.05) than in healthy. Circadian peak of TWA was found (90%) in a second part of day and at sleep (8%). Among them 60% (LQTS, BrS, and DCPM) had TWA > 55 microV.
Conclusion: Time-domain TWA during HM in children was independent of age, gender, and heart rate. In 94% healthy children, values of TWA do not exceed 55 microV but 20-50% children with cardiac pathology had TWA more than 55 microV. Night circadian type of TWA in diseases with risk of life-threatening arrhythmias associated with TWA was more than 55 microV.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prevalence of Microvolt T-Wave Alternans in Patients With Long QT Syndrome and Its Association With Torsade de Pointes.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016 Feb;9(2):e003206. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.115.003206. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26839386
-
Effect of beta-blockade on quantitative microvolt T-wave alternans in 24-hour continuous 12-lead ECG recordings in patients with long QT syndrome.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019 Jul;24(4):e12640. doi: 10.1111/anec.12640. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019. PMID: 30729628 Free PMC article.
-
Catecholamine-provoked microvoltage T wave alternans in genotyped long QT syndrome.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003 Aug;26(8):1660-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2003.t01-1-00249.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003. PMID: 12877697
-
[Microvolt T-wave alternant: pathomechanism and evaluation of a new marker of arrhythmia risk].Orv Hetil. 2010 Jul 25;151(30):1215-24. doi: 10.1556/OH.2010.28926. Orv Hetil. 2010. PMID: 20650812 Review. Hungarian.
-
Microvolt T-wave alternans: a review of techniques, interpretation, utility, clinical studies, and future perspectives.Int J Cardiol. 2006 May 24;109(3):293-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2005.06.049. Epub 2005 Jul 27. Int J Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16054250 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of electrocardiographic markers in children with dilated cardiomyopathy.Front Pediatr. 2022 Aug 23;10:917730. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.917730. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36081634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased microvolt T-wave alternans in children and adolescents with Eisenmenger syndrome.Anatol J Cardiol. 2018 May;19(5):303-310. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2018.60487. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Anatol J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29638226 Free PMC article.
-
T-Wave Alternans in Nonpathological Preterm Infants.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020 Jul;25(4):e12745. doi: 10.1111/anec.12745. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020. PMID: 31986237 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of standard versus orthogonal ECG leads for T-wave alternans identification.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2012 Apr;17(2):130-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2012.00490.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2012. PMID: 22537331 Free PMC article.
-
A Simulation Study of the Role of Mechanical Stretch in Arrhythmogenesis during Cardiac Alternans.Biophys J. 2021 Jan 5;120(1):109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.11.018. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 33248131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hearing H. Das Wesen des Herzalternans. Beat‐to‐beat T wave changes in experimental animal administration of glycolic acid. Munchen Med Wochenshr 1909;4:1417–1421.
-
- Lewis T. Notes upon alternation of the heart. QJ Med 1910;4:141–144.
-
- Nearing BD, Huang AH, Verrier RL. Dynamic tracking of cardiac vulnerability by complex demodulation of the T wave. Science 1991;252:437–440. - PubMed
-
- Kleinfeld MJ, Rozanski JJ. Alternans of the ST segment in Prinzmetal's angina. Circulation 1977;55:574–577. - PubMed
-
- Smith JM, Clancy EA, Valeri CR, et al Electrical alternans and cardiac electrical instability. Circulation 1988;77:110–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

