Accurate ECG diagnosis of atrial tachyarrhythmias using quantitative analysis: a prospective diagnostic and cost-effectiveness study
- PMID: 20522152
- PMCID: PMC2970682
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2010.01809.x
Accurate ECG diagnosis of atrial tachyarrhythmias using quantitative analysis: a prospective diagnostic and cost-effectiveness study
Abstract
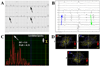
Quantitative ECG Analysis.
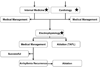
Introduction: Optimal atrial tachyarrhythmia management is facilitated by accurate electrocardiogram interpretation, yet typical atrial flutter (AFl) may present without sawtooth F-waves or RR regularity, and atrial fibrillation (AF) may be difficult to separate from atypical AFl or rapid focal atrial tachycardia (AT). We analyzed whether improved diagnostic accuracy using a validated analysis tool significantly impacts costs and patient care.
Methods and results: We performed a prospective, blinded, multicenter study using a novel quantitative computerized algorithm to identify atrial tachyarrhythmia mechanism from the surface ECG in patients referred for electrophysiology study (EPS). In 122 consecutive patients (age 60 ± 12 years) referred for EPS, 91 sustained atrial tachyarrhythmias were studied. ECGs were also interpreted by 9 physicians from 3 specialties for comparison and to allow healthcare system modeling. Diagnostic accuracy was compared to the diagnosis at EPS. A Markov model was used to estimate the impact of improved arrhythmia diagnosis. We found 13% of typical AFl ECGs had neither sawtooth flutter waves nor RR regularity, and were misdiagnosed by the majority of clinicians (0/6 correctly diagnosed by consensus visual interpretation) but correctly by quantitative analysis in 83% (5/6, P = 0.03). AF diagnosis was also improved through use of the algorithm (92%) versus visual interpretation (primary care: 76%, P < 0.01). Economically, we found that these improvements in diagnostic accuracy resulted in an average cost-savings of $1,303 and 0.007 quality-adjusted-life-years per patient.
Conclusions: Typical AFl and AF are frequently misdiagnosed using visual criteria. Quantitative analysis improves diagnostic accuracy and results in improved healthcare costs and patient outcomes.
© 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Camm AJ, Campbell WB, Haines DE, Kuck KH, Lerman BB, Miller DD, Shaeffer CW, Stevenson WG, Tomaselli GF, Antman EM, Smith SC, Jr, Alpert JS, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gibbons RJ, Gregoratos G, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Jacobs AK, Russell RO, Jr, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Burgos EF, Cowie M, Deckers JW, Garcia MA, Klein WW, Lekakis J, Lindahl B, Mazzotta G, Morais JC, Oto A, Smiseth O, Trappe HJ. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary. a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines and the European society of cardiology committee for practice guidelines (writing committee to develop guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias) developed in collaboration with NASPE-Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1493–1531. - PubMed
-
- Chugh SS, Blackshear JL, Shen WK, Hammill SC, Gersh BJ. Epidemiology and natural history of atrial fibrillation: clinical implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Bochoeyer A, Yang Y, Cheng J, Lee RJ, Keung EC, Marrouche NF, Natale A, Scheinman MM. Surface electrocardiographic characteristics of right and left atrial flutter. Circulation. 2003;108:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Krummen DE, Feld GK, Narayan SM. Diagnostic Accuracy of Irregularly Irregular RR Intervals in Separating Atrial Fibrillation from Atrial Flutter. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98:209–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

