Potential down-regulation of salivary gland AQP5 by LPS via cross-coupling of NF-kappaB and p-c-Jun/c-Fos
- PMID: 20522648
- PMCID: PMC2913374
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090282
Potential down-regulation of salivary gland AQP5 by LPS via cross-coupling of NF-kappaB and p-c-Jun/c-Fos
Abstract
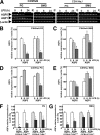
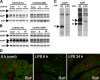
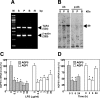
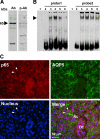
The mRNA and protein levels of aquaporin (AQP)5 in the parotid gland were found to be potentially decreased by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in vivo in C3H/HeN mice, but only weakly in C3H/HeJ, a TLR4 mutant mouse strain. In the LPS-injected mice, pilocarpine-stimulated saliva production was reduced by more than 50%. In a tissue culture system, the LPS-induced decrease in the AQP5 mRNA level was blocked completely by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, MG132, tyrphostin AG126, SP600125, and partially by SB203580, which are inhibitors for IkappaB kinase, 26S proteasome, ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK, respectively. In contrast, the expression of AQP1 mRNA was down-regulated by LPS and such down-regulation was blocked only by SP600125. The transcription factors NF-kappaB (p65 subunit), p-c-Jun, and c-Fos were increased by LPS given in vivo, whereas the protein-binding activities of the parotid gland extract toward the sequences for NF-kappaB but not AP-1-responsive elements present at the promoter region of the AQP5 gene were increased by LPS injection. Co-immunoprecipitation by using antibody columns suggested the physical association of the three transcription factors. These results suggest that LPS-induced potential down-regulation of expression of AQP5 mRNA in the parotid gland is mediated via a complex(es) of these two classes of transcription factors, NF-kappaB and p-c-Jun/c-Fos.
Figures


References
-
- Yakata K, Hiroaki Y, Ishibashi K, Sohara E, Sasaki S, Mitsuoka K, Fujiyoshi Y. Aquaporin-11 containing a divergent NPA motif has normal water channel activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768:688–693. - PubMed
-
- Itoh A, Tsujikawa T, Fujiyama Y, Bamba T. Enhancement of aquaporin-3 by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in a human colonic epithelial cell line. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;18:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Verkman AS. Physiological importance of aquaporins: lessons from knockout mice. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2000;9:517–522. - PubMed
-
- Marinelli RA, Tietz PS, Pham LD, Rueckert L, Agre P, LaRusso NF. Secretin induces the apical insertion of aquaporin-1 water channels in rat cholangiocytes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 1999;276:G280–G286. - PubMed
-
- Steinfeld S, Cogan E, King LS, Agre P, Kiss R, Delporte C. Abnormal distribution of aquaporin-5 water channel protein in salivary glands from Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Lab Invest. 2001;81:143–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

