Maintenance treatment of renal anaemia in haemodialysis patients with methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta versus darbepoetin alfa administered monthly: a randomized comparative trial
- PMID: 20522670
- PMCID: PMC2989790
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfq305
Maintenance treatment of renal anaemia in haemodialysis patients with methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta versus darbepoetin alfa administered monthly: a randomized comparative trial
Abstract
Background: Several studies with erythropoiesis-stimulating agents claim that maintenance therapy of renal anaemia may be possible at extended dosing intervals; however, few studies were randomized, results varied, and comparisons between agents were absent. We report results of a multi-national, randomized, prospective trial comparing haemoglobin maintenance with methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa administered once monthly.
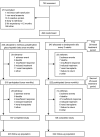
Methods: Haemodialysis patients (n = 490) on stable once-weekly intravenous darbepoetin alfa were randomized to methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta once monthly or darbepoetin alfa every 2 weeks for 26 weeks, with dose adjustment for individual haemoglobin target (11-13 g/dL; maximum decrease from baseline 1 g/dL). Subsequently, patients entered a second 26-week period of once-monthly methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta and darbepoetin alfa. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who maintained average haemoglobin ≥10.5 g/dL, with a decrease from baseline ≤1 g/dL, in Weeks 50-53; the secondary endpoint was dose change over time. The trial is registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00394953.
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar between groups. One hundred and fifty-seven of 245 patients treated with methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta and 99 of 245 patients with darbepoetin alfa met the response definition (64.1% and 40.4%; P < 0.0001). Doses increased by 6.8% with methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta and 58.8% with darbepoetin alfa during once-monthly treatment. Death rates were equal between treatments (5.7%). Most common adverse events included hypertension, procedural hypotension, nasopharyngitis and muscle spasms, with no differences between groups.
Conclusions: Methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta maintained target haemoglobin more successfully than darbepoetin alfa at once-monthly dosing intervals despite dose increases with darbepoetin alfa.
Figures
References
-
- Locatelli F, Aljama P, Bárány P, et al. European Best Practice Guidelines Working Group Revised European best practice guidelines for the management of anaemia in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19 (suppl 2):ii1–ii47. - PubMed
-
- Leaf DE, Goldfarb DS. Interpretation and review of health-related quality of life data in CKD patients receiving treatment for anemia. Kidney Int. 2009;75:15–24. - PubMed
-
- Neorecormon Summary of Product Characteristics. 2009 Available at: http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/Neorecormon/H-116-PI-en.pdf.
-
- Mahon A, Docherty B. Renal anaemia—the patient experience. EDTNA ERCA J. 2004;30:34–37. - PubMed
-
- 2007 Annual data report: atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. United States Renal Data System. 2007 Available at: http://www.usrds.org/atlas_2007.htm. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous