Local thermal control of the human cutaneous circulation
- PMID: 20522732
- PMCID: PMC2963328
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00407.2010
Local thermal control of the human cutaneous circulation
Abstract
The level of skin blood flow is subject to both reflex thermoregulatory control and influences from the direct effects of warming and cooling the skin. The effects of local changes in temperature are capable of maximally vasoconstricting or vasodilating the skin. They are brought about by a combination of mechanisms involving endothelial, adrenergic, and sensory systems. Local warming initiates a transient vasodilation through an axon reflex, succeeded by a plateau phase due largely to nitric oxide. Both phases are supported by sympathetic transmitters. The plateau phase is followed by the die-away phenomenon, a slow reversal of the vasodilation that is dependent on intact sympathetic vasoconstrictor nerves. The vasoconstriction with local skin cooling is brought about, in part, by a postsynaptic upregulation of α(2c)-adrenoceptors and, in part, by inhibition of the nitric oxide system at at least two points. There is also an early vasodilator response to local cooling, dependent on the rate of cooling. The mechanism for that transient vasodilation is not known, but it is inhibited by intact sympathetic vasoconstrictor nerve function and by intact sensory nerve function.
Figures
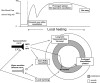
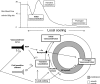
References
-
- Alvarez GE, Zhao K, Kosiba WA, Johnson JM. Relative roles of local and reflex components in cutaneous vasoconstriction during skin cooling in humans. J Appl Physiol 100: 2083–2088, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Angus JA, Cocks TM, Satoh K. The alpha adrenoceptors on endothelial cells. Fed Proc 45: 2355–2359, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Bailey SR, Eid AH, Mitra S, Flavahan S, Flavahan NA. Rho kinase mediates cold-induced constriction of cutaneous arteries. Circ Res 94: 1367–1374, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bailey SR, Mitra S, Flavahan S, Flavahan NA. Reactive oxygen species from smooth muscle mitochondria initiate cold-induced constriction of cutaneous arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289: H243–H250, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

