Induction of fear extinction with hippocampal-infralimbic BDNF
- PMID: 20522777
- PMCID: PMC3570764
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1186909
Induction of fear extinction with hippocampal-infralimbic BDNF
Abstract
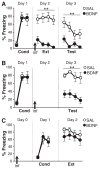
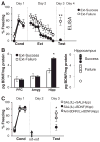
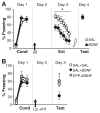
The extinction of conditioned fear memories requires plasticity in the infralimbic medial prefrontal cortex (IL mPFC), but little is known about the molecular mechanisms involved. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a key mediator of synaptic plasticity in multiple brain areas. In rats subjected to auditory fear conditioning, BDNF infused into the IL mPFC reduced conditioned fear for up to 48 hours, even in the absence of extinction training, which suggests that BDNF substituted for extinction. Similar to extinction, BDNF-induced reduction in fear required N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and did not erase the original fear memory. Rats failing to learn extinction showed reduced BDNF in hippocampal inputs to the IL mPFC, and augmenting BDNF in this pathway prevented extinction failure. Hence, boosting BDNF activity in hippocampal-infralimbic circuits may ameliorate disorders of learned fear.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR003051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH058883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH058883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081975/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH058883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS043011/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MH081975/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083516/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007600/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS043011/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH083516/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH085383/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 MH085383/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R29 MH058883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

