Smad3 signaling critically regulates fibroblast phenotype and function in healing myocardial infarction
- PMID: 20522804
- PMCID: PMC2917472
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.216101
Smad3 signaling critically regulates fibroblast phenotype and function in healing myocardial infarction
Abstract
Rationale: Cardiac fibroblasts are key effector cells in the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta/Smad3 signaling is activated in the border zone of healing infarcts and induces fibrotic remodeling of the infarcted ventricle contributing to the development of diastolic dysfunction.
Objective: The present study explores the mechanisms responsible for the fibrogenic effects of Smad3 by dissecting its role in modulating cardiac fibroblast phenotype and function.
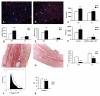
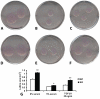
Methods and results: Smad3 null mice and corresponding wild-type controls underwent reperfused myocardial infarction protocols. Surprisingly, reduced collagen deposition in Smad3-/- infarcts was associated with increased infiltration with myofibroblasts. In vitro studies demonstrated that TGF-beta1 inhibited murine cardiac fibroblast proliferation; these antiproliferative effects were mediated via Smad3. Smad3-/- fibroblasts were functionally defective, exhibiting impaired collagen lattice contraction when compared with wild-type cells. Decreased contractile function was associated with attenuated TGF-beta-induced expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin. In addition, Smad3-/- fibroblasts had decreased migratory activity on stimulation with serum, and exhibited attenuated TGF-beta1-induced upregulation of extracellular matrix protein synthesis. Upregulation of connective tissue growth factor, an essential downstream mediator in TGF-beta-induced fibrosis, was in part dependent on Smad3. Connective tissue growth factor stimulation enhanced extracellular matrix protein expression by cardiac fibroblasts in a Smad3-independent manner.
Conclusions: Disruption of Smad3 results in infiltration of the infarct with abundant hypofunctional fibroblasts that exhibit impaired myofibroblast transdifferentiation, reduced migratory potential, and suppressed expression of fibrosis-associated genes.
Figures






References
-
- Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:349–363. - PubMed
-
- Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J Pathol. 2003;200:500–503. - PubMed
-
- Hinz B. Formation and function of the myofibroblast during tissue repair. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:526–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

