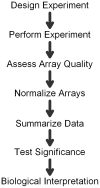
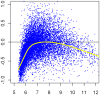
Making informed choices about microarray data analysis
- PMID: 20523743
- PMCID: PMC2877726
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000786
Making informed choices about microarray data analysis
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Slonim DK, Yanai I. Getting started in gene expression microarray analysis. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009;5:e1000543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000543. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser C Ser B. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Ayroles JF, Gibson G. Analysis of variance of microarray data. Methods Enzymol. 2006;411:214–233. - PubMed
-
- Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 2007;8:118–127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

