Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
- PMID: 20523788
- PMCID: PMC2861215
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.203
Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
Abstract
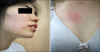
Food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is the triggering of anaphylaxis after ingestion of certain foods when followed by physical exercise. Symptoms vary from the typical generalized urticaria to severe allergic reactions. We report the case of a 20-year-old woman who had a 7-year history of recurrent wheals and dyspnea after ingesting several kinds of food (wheat, pork, and beef) along with physical exercise. Based on a provocation test, she was diagnosed with wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis. She was instructed to take 2 mg of ketotifen 2 hours before ingestion of wheat to prevent the symptoms, and subsequently the provocation test did not elicit wheals. We therefore prescribed ketotifen (1 mg twice a day). She has not had recurrent wheals or dyspnea for 6 months. We herein report an interesting case of wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis with successful prevention by ketotifen.
Keywords: Food-dependent; Ketotifen; Wheat; exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis with a high level of plasma noradrenaline.J Dermatol. 2007 Feb;34(2):110-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2006.00227.x. J Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17239147
-
[Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: case report and review of literature.].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2009 Dec;32(12):923-5. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 20193353 Review. Chinese.
-
[FOOD-DEPENDENT EXERCISE-INDUCED ANAPHYLAXIS IMPROVED BY OMALIZUMAB PRESCRIBED FOR IDIOPATHIC CHRONIC URTICARIA].Arerugi. 2022;71(1):46-50. doi: 10.15036/arerugi.71.46. Arerugi. 2022. PMID: 35173125 Japanese.
-
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: influence of concurrent aspirin administration on skin testing and provocation.Br J Dermatol. 2002 Mar;146(3):466-72. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04601.x. Br J Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 11952547
-
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis.J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Aug;47(2):109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.03.004. Epub 2007 May 15. J Dermatol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17507204 Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis: Literature Review and Recent Updates.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018 Oct 26;18(12):72. doi: 10.1007/s11882-018-0830-6. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018. PMID: 30367321 Review.
-
Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: A clinical view.Ital J Pediatr. 2012 Sep 14;38:43. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-38-43. Ital J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22980517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Getting in Shape: Updates in Exercise Anaphylaxis.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Nov;24(11):631-638. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01176-4. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 39294451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: an update on diagnosis and treatment.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011 Feb;11(1):45-51. doi: 10.1007/s11882-010-0150-y. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011. PMID: 20922508 Free PMC article.
-
Food-dependent, exercise-induced gastrointestinal distress.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2011 Sep 28;8:12. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-8-12. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21955383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chong SU, Worm M, Zuberbier T. Role of adverse reactions to food in urticaria and exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002;129:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979;63:433–434. - PubMed
-
- Aihara Y, Takahashi Y, Kotoyori T, Mitsuda T, Ito R, Aihara M, et al. Frequency of food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese junior-high-school students. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:1035–1039. - PubMed
-
- Shadick NA, Liang MH, Partridge AJ, Bingham C, Wright E, Fossel AH, et al. The natural history of exercise-induced anaphylaxis: survey results from a 10-year follow-up study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;104:123–127. - PubMed
-
- Morita E, Kunie K, Matsuo H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;47:109–117. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources