Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
- PMID: 20523788
- PMCID: PMC2861215
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.203
Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
Abstract
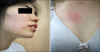
Food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is the triggering of anaphylaxis after ingestion of certain foods when followed by physical exercise. Symptoms vary from the typical generalized urticaria to severe allergic reactions. We report the case of a 20-year-old woman who had a 7-year history of recurrent wheals and dyspnea after ingesting several kinds of food (wheat, pork, and beef) along with physical exercise. Based on a provocation test, she was diagnosed with wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis. She was instructed to take 2 mg of ketotifen 2 hours before ingestion of wheat to prevent the symptoms, and subsequently the provocation test did not elicit wheals. We therefore prescribed ketotifen (1 mg twice a day). She has not had recurrent wheals or dyspnea for 6 months. We herein report an interesting case of wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis with successful prevention by ketotifen.
Keywords: Food-dependent; Ketotifen; Wheat; exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA).
Figures
References
-
- Chong SU, Worm M, Zuberbier T. Role of adverse reactions to food in urticaria and exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002;129:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979;63:433–434. - PubMed
-
- Aihara Y, Takahashi Y, Kotoyori T, Mitsuda T, Ito R, Aihara M, et al. Frequency of food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese junior-high-school students. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:1035–1039. - PubMed
-
- Shadick NA, Liang MH, Partridge AJ, Bingham C, Wright E, Fossel AH, et al. The natural history of exercise-induced anaphylaxis: survey results from a 10-year follow-up study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;104:123–127. - PubMed
-
- Morita E, Kunie K, Matsuo H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;47:109–117. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources