Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser Therapy of Acquired Bilateral Nevus of Ota-like Macules
- PMID: 20523799
- PMCID: PMC2861240
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.255
Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser Therapy of Acquired Bilateral Nevus of Ota-like Macules
Abstract
Background: Acquired bilateral nevus of Ota-like macules (ABNOM) is a dermal pigmented lesion common in individuals of Oriental origin. The Q-switched Nd:YAG laser (QSNYL) has been used successfully to treat a variety of benign, dermal, pigmented lesions, including nevus of Ota lesions. The similarity between ABNOM and nevus of Ota suggested that QSNYL may also be effective in the former.
Objective: To determine the efficacy and side-effect profiles of QSNYL treatment of ABNOM in Korean patients.
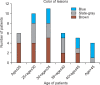
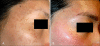
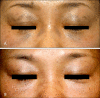
Methods: Of 42 Korean patients with ABNOM, 29 were treated with QSNYL (1,064 nm, 3 mm spot size, fluence 8~9.5 J/cm(2)), for up to 10 sessions each. Clinical photographs were taken before and after treatment. Lesion clearance was graded and complications such as hyperpigmentation, scarring, hypopigmentation, and erythema were assessed.
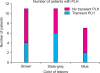
Results: Of the 29 treated patients, 19 (66%) showed excellent or good results. Of the patients who were treated more than 3 times, 76% showed good to excellent results. Two patients experienced post-laser hyperpigmentation (PLH), which persisted for more than one month, but no patient experienced persistent erythema or hypertrophic scarring.
Conclusion: QSNYL is safe and effective in the treatment of ABNOM in Korean patients. Short-interval repetitive treatment is especially useful in improving therapeutic results and reducing PLH.
Keywords: Acquired bilateral nevus of Ota-like macules; Q-switched Nd:YAG laser.
Figures

References
-
- Hori Y, Kawashima M, Oohara K, Kukita A. Acquired, bilateral nevus of Ota-like macules. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10:961–964. - PubMed
-
- Hori Y, Takayama O. Circumscribed dermal melanoses. Classification and histologic features. Dermatol Clin. 1988;6:315–326. - PubMed
-
- Kunachak S, Kunachakr S, Sirikulchayanonta V, Leelaudomniti P. Dermabrasion is an effective treatment for acquired bilateral nevus of Ota-like macules. Dermatol Surg. 1996;22:559–562. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg DJ, Nychay SG. Q-switched ruby laser treatment of nevus of Ota. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1992;18:817–821. - PubMed
-
- Geronemus RG. Q-switched ruby laser therapy of nevus of Ota. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:1618–1622. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

