Summarizing the evidence on the international trade in illegal wildlife
- PMID: 20524140
- PMCID: PMC7087942
- DOI: 10.1007/s10393-010-0317-y
Summarizing the evidence on the international trade in illegal wildlife
Abstract
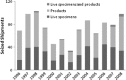
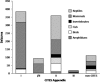
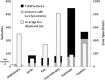
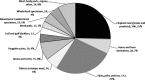
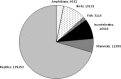
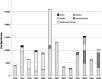
The global trade in illegal wildlife is a multi-billion dollar industry that threatens biodiversity and acts as a potential avenue for invasive species and disease spread. Despite the broad-sweeping implications of illegal wildlife sales, scientists have yet to describe the scope and scale of the trade. Here, we provide the most thorough and current description of the illegal wildlife trade using 12 years of seizure records compiled by TRAFFIC, the wildlife trade monitoring network. These records comprise 967 seizures including massive quantities of ivory, tiger skins, live reptiles, and other endangered wildlife and wildlife products. Most seizures originate in Southeast Asia, a recently identified hotspot for future emerging infectious diseases. To date, regulation and enforcement have been insufficient to effectively control the global trade in illegal wildlife at national and international scales. Effective control will require a multi-pronged approach including community-scale education and empowering local people to value wildlife, coordinated international regulation, and a greater allocation of national resources to on-the-ground enforcement.
Figures

References
-
- Amin R, Thomas K, Emslie RH, Foose TJ, Van Strien N. An overview of the conservation status of and threats to rhinoceros species in the wild. International Zoo Yearbook. 2006;40:96–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1090.2006.00096.x. - DOI
-
- ASEAN-WEN (2009) www.asean-wen.org. Accessed 23 June 2009
-
- Bailey TA, Silvanose CD, Naldo J, Combreau O, Launay F, Wernery U, Kinne J, Gough R, Manvell R (1999) Health considerations of the rehabilitation of illegally traded houbara bustards Chlamydotis undulata macqueenii in the Middle East. European Association of Avian Veterinarians Conference, Italy, 1999
-
- Cheung SN, Dudgeon D. Quantifying the Asian turtle crisis: market surveys in southern China, 2000–2003. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems. 2006;16:751–770. doi: 10.1002/aqc.803. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

