NR2B-NMDA receptor-mediated increases in intracellular Ca2+ concentration regulate the tyrosine phosphatase, STEP, and ERK MAP kinase signaling
- PMID: 20524968
- PMCID: PMC3049732
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06835.x
NR2B-NMDA receptor-mediated increases in intracellular Ca2+ concentration regulate the tyrosine phosphatase, STEP, and ERK MAP kinase signaling
Abstract
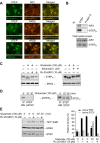
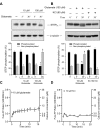
NMDA receptors regulate both the activation and inactivation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling cascade, a key pathway involved in neuronal plasticity and survival. This bi-directional regulation of ERK activity by NMDA receptors has been attributed to opposing actions of NR2A- versus NR2B-containing NMDA receptors, but how this is implemented is not understood. Here, we show that glutamate-mediated intracellular Ca(2+) increases occur in two phases, a rapid initial increase followed by a delayed larger increase. Both phases of the Ca(2+) increase were blocked by MK-801, a non-selective NMDA receptor inhibitor. On the other hand, selective inhibition of NR2B-NMDA receptors by Ifenprodil or Ro 25-6981 blocked the delayed larger phase but had only a small effect on the rapid initial increase. The rapid initial increase in Ca(2+), presumably because of NR2A-NMDAR activation, was sufficient to activate ERK, whereas the large delayed increases in Ca(2+) mediated by NR2B-NMDARs were necessary for dephosphorylation and subsequent activation of striatal-enriched phosphatase, a neuron-specific tyrosine phosphatase that in turn mediates the dephosphorylation and inactivation of ERK. We conclude that the magnitude of Ca(2+) increases mediated through NR2B-NMDA receptors plays a critical role in the regulation of the serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases and phosphatases that are involved in the regulation of ERK activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NMDA-mediated activation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP regulates the duration of ERK signaling.Nat Neurosci. 2003 Jan;6(1):34-42. doi: 10.1038/nn989. Nat Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12483215
-
Bi-directional regulation of CaMKIIα phosphorylation at Thr286 by NMDA receptors in cultured cortical neurons.J Neurochem. 2012 Jul;122(2):295-307. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07787.x. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22582824 Free PMC article.
-
NR2B-NMDA receptor mediated modulation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP regulates glutamate induced neuronal cell death.J Neurochem. 2010 Dec;115(6):1350-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07035.x. Epub 2010 Nov 2. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 21029094 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
-
Somatostatin receptor 1 (SSTR1)-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation correlates with the activation of the MAP kinase cascade: role of the phosphotyrosine phosphatase SHP-2.J Physiol Paris. 2000 May-Aug;94(3-4):239-50. doi: 10.1016/s0928-4257(00)00214-x. J Physiol Paris. 2000. PMID: 11088001 Review.
Cited by
-
Competing mechanisms of plasticity impair compensatory responses to repetitive apnoea.J Physiol. 2019 Aug;597(15):3951-3967. doi: 10.1113/JP277676. Epub 2019 Jul 7. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31280489 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective role of a brain-enriched tyrosine phosphatase, STEP, in focal cerebral ischemia.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 6;33(45):17814-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2346-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24198371 Free PMC article.
-
REM Sleep Regulating Mechanisms in the Cholinergic Cell Compartment of the Brainstem.Indian J Sleep Med. 2013;8(2):58-66. doi: 10.5958/j.0974-0155.8.2.009. Indian J Sleep Med. 2013. PMID: 25400382 Free PMC article.
-
H2O2 attenuates IGF-1R tyrosine phosphorylation and its survival signaling properties in neuronal cells via NR2B containing NMDA receptor.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(39):65313-65328. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18625. eCollection 2017 Sep 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29029433 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Houttuyfonate Prevents Seizures and Neuronal Cell Loss by Maintaining Glutamatergic System Stability in Male Rats with Kainic Acid-Induced Seizures.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 13;12(6):1312. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061312. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auberson YP, Allgeier H, Bischoff S, Lingenhoehl K, Moretti R, Schmutz M. 5-Phosphonomethylquinoxalinediones as competitive NMDA receptor antagonists with a preference for the human 1A/2A, rather than 1A/2B receptor composition. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters. 2002;12:1099–1102. - PubMed
-
- Banko JL, Hou L, Klann E. NMDA receptor activation results in PKA- and ERK-dependent Mnk1 activation and increased eIF4E phosphorylation in hippocampal area CA1. Journal of neurochemistry. 2004;91:462–470. - PubMed
-
- Bath CP, Farrell LN, Gilmore J, Ward MA, Hicks CA, O'Neill MJ, Bleakman D. The effects of ifenprodil and eliprodil on voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and in gerbil global cerebral ischaemia. European journal of pharmacology. 1996;299:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer NH. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. Journal of neurochemistry. 1984;43:1369–1374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

