The α-granule proteome: novel proteins in normal and ghost granules in gray platelet syndrome
- PMID: 20524979
- PMCID: PMC2953603
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03932.x
The α-granule proteome: novel proteins in normal and ghost granules in gray platelet syndrome
Abstract
Background: Deficiencies in granule-bound substances in platelets cause congenital bleeding disorders known as storage pool deficiencies. For disorders such as gray platelet syndrome (GPS), in which thrombocytopenia, enlarged platelets and a paucity of α-granules are observed, only the clinical and histologic states have been defined.
Objectives: In order to understand the molecular defect in GPS, the α-granule fraction protein composition from a normal individual was compared with that of a GPS patient by mass spectrometry (MS).
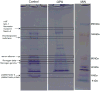
Methods: Platelet organelles were separated by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation. Proteins from sedimented fractions were separated by sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, reduced, alkylated, and digested with trypsin. Peptides were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem MS. Mascot was used for peptide/protein identification and to determine peptide false-positive rates. MassSieve was used to generate and compare parsimonious lists of proteins.
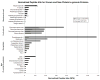
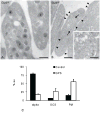
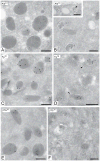
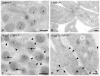
Results: As compared with control, the normalized peptide hits (NPHs) from soluble, biosynthetic α-granule proteins were markedly decreased or undetected in GPS platelets, whereas the NPHs from soluble, endocytosed α-granule proteins were only moderately affected. The NPHs from membrane-bound α-granule proteins were similar in normal platelets and GPS platelets, although P-selectin and Glut3 were slightly decreased, consistent with immunoelectron microscopy findings in resting platelets. We also identified proteins not previously known to be decreased in GPS, including latent transforming growth factor-β-binding protein 1(LTBP1), a component of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) complex.
Conclusions: Our results support the existence of 'ghost granules' in GPS, point to the basic defect in GPS as failure to incorporate endogenously synthesized megakaryocytic proteins into α-granules, and identify specific new proteins as α-granule inhabitants.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00001846 NCT00369421.
© 2010 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Clinical proteomics in platelet research: challenges ahead.J Thromb Haemost. 2010 Aug;8(8):1784-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03949.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20553383 No abstract available.
References
-
- Smith MP, Cramer EM, Savidge GF. Megakaryocytes and platelets in alpha-granule disorders. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1997;10:125–48. - PubMed
-
- Raccuglia G. Gray platelet syndrome. A variety of qualitative platelet disorder. The American journal of medicine. 1971;51:818–28. - PubMed
-
- Harrison P, Cramer EM. Platelet alpha-granules. Blood reviews. 1993;7:52–62. - PubMed
-
- Tubman VN, Levine JE, Campagna DR, Monahan-Earley R, Dvorak AM, Neufeld EJ, Fleming MD. X-linked gray platelet syndrome due to a GATA1 Arg216Gln mutation. Blood. 2007;109:3297–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

