Nutritively sweetened beverage consumption and body weight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized experiments
- PMID: 20524996
- PMCID: PMC3169649
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2010.00755.x
Nutritively sweetened beverage consumption and body weight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized experiments
Abstract
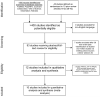
Nutritively sweetened beverages (NSBs) may play a role in the obesity epidemic. We abstracted data from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and evidence-based reviews through January 2009 concerning effects of consumption of NSBs on changes in body weight and adiposity. Studies included were those (i) conducted in humans; (ii) lasting at least 3 weeks; (iii) incorporating random assignment of subjects to conditions that differed only in the consumption of NSBs and (iv) including an adiposity indicator as an outcome. Twelve studies met the inclusion criteria. Meta-analysis of six studies that added NSBs to persons' diets showed dose-dependent increases in weight. Contrarily, meta-analysis of studies that attempted to reduce NSB consumption consistently showed no effect on body mass index (BMI) when all subjects were considered. Meta-analysis of studies providing access to results separately for subjects overweight at baseline showed a significant effect of a roughly 0.35 standard deviations lesser BMI change (i.e. more weight loss or less weight gain) relative to controls. The current evidence does not demonstrate conclusively that NSB consumption has uniquely contributed to obesity or that reducing NSB consumption will reduce BMI levels in general. We recommend an adequately powered RCT with overweight persons, for whom there is suggestive evidence of an effect.
© 2010 The Authors. obesity reviews © 2010 International Association for the Study of Obesity.
Figures





References
-
- Gillis LJ, Bar-Or O. Food away from home, sugar-sweetened drink consumption and juvenile obesity. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003;22(6):539–45. - PubMed
-
- Belpoggi F, Soffritti M, Tibaldi E, Falcioni L, Bua L, Trabucco F. Results of long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on Coca-Cola administered to Sprague-Dawley rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1076:736–52. - PubMed
-
- Ogur R, Uysal B, Ogur T, et al. Evaluation of the effect of cola drinks on bone mineral density and associated factors. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;100(5):334–8. - PubMed
-
- Mourao DM, Bressan J, Campbell WW, Mattes RD. Effects of food form on appetite and energy intake in lean and obese young adults. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007;31(11):1688–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

