Stress and childhood asthma risk: overlapping evidence from animal studies and epidemiologic research
- PMID: 20525123
- PMCID: PMC2869338
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-4-1-29
Stress and childhood asthma risk: overlapping evidence from animal studies and epidemiologic research
Abstract
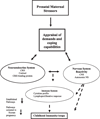
: Rapidly expanding evidence increasingly strengthens the evidence linking psychological factors to asthma and allergy expression. Parallel studies in animals and humans demonstrating the influence of prenatal maternal stress and early caregiving experiences on the disrupted regulation of defensive biological systems [eg, sympathetic and adrenomedullary (SAM) system and the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis] provide strong proof of concept for this line of research. The consequent altered neuroimmune responses may influence the expression of immune-mediated disorders such as asthma as well as enhance an individual's susceptibility to other environmental factors that may also contribute to asthma risk.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prenatal maternal stress and early caregiving experiences: implications for childhood asthma risk.Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2007 Nov;21 Suppl 3:8-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3016.2007.00879.x. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2007. PMID: 17935570
-
Altered responsiveness of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis and the sympathetic adrenomedullary system to stress in patients with atopic dermatitis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Sep;87(9):4245-51. doi: 10.1210/jc.2001-010872. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12213879
-
Linking the hemodynamic consequences of adverse childhood experiences to an altered HPA axis and acute stress response.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Mar;93:254-263. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.018. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33358983 Review.
-
Early environmental regulation of forebrain glucocorticoid receptor gene expression: implications for adrenocortical responses to stress.Dev Neurosci. 1996;18(1-2):49-72. doi: 10.1159/000111395. Dev Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8840086 Review.
-
Early-life adversity programs long-term cytokine and microglia expression within the HPA axis in female Japanese quail.J Exp Biol. 2019 Mar 21;222(Pt 6):jeb187039. doi: 10.1242/jeb.187039. J Exp Biol. 2019. PMID: 30814294
Cited by
-
Birthing parent adverse childhood experiences and risk of atopic diseases in 5-year-old children.Front Allergy. 2025 Jan 7;5:1483911. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2024.1483911. eCollection 2024. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 39845651 Free PMC article.
-
The association between neuraxial anesthesia and the development of childhood asthma - a secondary analysis of the newborn epigenetics study cohort.Curr Med Res Opin. 2020 Jun;36(6):1025-1032. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2020.1747417. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020. PMID: 32212939 Free PMC article.
-
Depressive symptoms and the incidence of adult-onset asthma in African American women.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014 Apr;112(4):333-8.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2013.12.025. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24440322 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between psychosocial stress, child's anxiety, and lung function in mid-childhood.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 Nov;133(5):568-573.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2024.07.030. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39117147
-
Asthma and wheezing are associated with depression and anxiety in adults: an analysis from 54 countries.Pulm Med. 2013;2013:929028. doi: 10.1155/2013/929028. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Pulm Med. 2013. PMID: 23577252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wright RJ, Fisher EB. In: Neighborhoods and health. Kawachi I, Berkman LF, editor. New York: Oxford University Press; 2003. Putting asthma into context: influences on risk, behavior, and intervention; pp. 233–62. full_text.
-
- Summary of the Symposium on Genetic Variation and Gene Environment Interaction in Human Health and Disease. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) and National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) http://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/science/gene-env/docs/gesymp03.pdf (accessed November 30, 2007).
-
- Hernandez LM, Blazer DG, editor. Committee on Assessing Interactions Among Social, Behavioral and Genetic Factors in Health. Genes, behavior, and the social environment: moving beyond the nature/nurture debate. Washington (DC): Institute of Medicine of the National Academies; 2006. pp. 109–31.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources